[toc]Fibrinolytic drugs are those capable of stimulating the dissolution of a blood clot (thrombus). They’re administered by IV. Examples include Abbokinase (generic name: urokinase) which is used for blood clots in the lungs, and Streptase (streptokinase) used for heart attacks and deep vein thrombosis.
Dr. Sumi, a professor at Kurashiki University in Japan, conducted research on 172 different foods from around the world that have (or are suspected to have) fibrinolytic activity.
He and his team reported that natto had the highest fibrinolytic activity among all the foods tested. (1) (2)
What is nattokinase?
Natto is a traditional Japanese food made from soybeans fermented with a bacteria called Bacillus subtilis var. natto (formally known as Bacillus natto). This fermentation produces the enzyme nattokinase, which is responsible for natto’s fibrinolytic activity.
Despite its name, the nattokinase mechanism of action is not as a kinase enzyme. (3)
Kinase enzymes work by adding phosphates to certain proteins, which helps dissolve blood clots. An example is urokinase, which is naturally produced by the kidneys and synthetically created for use in medicine.
How nattokinase works is as a serine protease. That means it breaks up certain proteins found in blood clots into smaller fragments. It has not been tested on actual blood clots in humans. Only the effects on risk factors have been clinically studied.
Natto originated in Japan and has been consumed there for over 1,000 years. The fermentation creates long stringy and slimy “threads” which stick to the beans. The Japanese eat it for breakfast. You will find no other cultures in the world doing the same.. it’s definitely an acquired taste!
What makes natto unique versus their other Japanese fermented foods – like miso, shoyu, and tempeh – is that bacteria are used, instead for fungi/yeasts.
Since only a specific strain of bacteria can produce it, the list of foods high in nattokinase is quite short; only natto. No other foods contain nattokinase. Other types of bacteria are used to ferment kimchi, yogurt, kefir, and kombucha.
The fermented Korean soybean paste known as cheonggukjang is the closest thing; it’s also made with Bacillus subtilis bacteria but not the same strain used to make natto. Other fibrinolytic enzymes have been reported for cheonggukjang. (4)
Nattokinase supplements are sold as capsules, tablets, and bulk powder. They can be organic and raw if derived from the food source, but they will be of low concentration since other enzymes and ingredients are present.
Today, most supplements ferment the bacteria in a controlled environment to make a potent dosage of nattokinase. Some combine it with an enzyme made by silk worms called serrapeptase (e.g. Doctor’s Best Natto-Serra), an enzyme from earth worms (lumbrokinase), vitamin K2 (MK-7 form), L-theanine (Suntheanine) and/or pine bark extract (Pycnogenol).
FAQs
Is nattokinase the same as vitamin K2?
No. While it’s true there’s K2 in natto, that’s something completely different than the nattokinase it contains.
The confusion stems from the fact that vitamin K2 (MK-7) supplements often add nattokinase. Vitamin K plays an important role in circulation, coagulation, and anti-coagulation of the blood. That’s why brands like Jarrow Formulas and NOW Foods combine the two.
What does nattokinase do for the body?
It is believed that nattokinase may act as an anticoagulant, which means it might help prevent blood clots.
This is why some people believe nattokinase vs. aspirin (low-dose) is a better choice, but there is not yet research to prove that opinion. On the other hand, daily low dose aspirin regimens of 81 mg are well-studied and backed by positive results.
What nattokinase is good for in the human body, if anything, remains unknown. Five human clinical trials have been published relating to anti-coagulation, edema, superficial and deep vein thrombosis, high cholesterol and triglycerides, high blood pressure, and patients undergoing dialysis. There is too little clinical data on any one potential benefit to draw a conclusion.
Some people have suggested theoretical – yet untested – potential for atrial fibrillation (AFib), brain health, depression, endometriosis, Lyme disease, fertility, glaucoma, gout, hair growth, headaches (including migraines), joint pain from inflammation, ovarian cysts, uterine fibroids, weight loss, and the side effect of lymphedema in arms and legs from cancer treatment. The vast majority of these are highly speculative and not supported by any science.
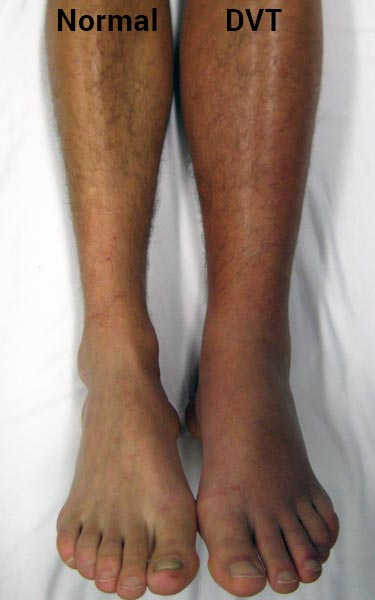
The best evidence is for diseases and conditions more directly related to blood clotting. Things like deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolisms, and perhaps varicose veins. Science also suggests it might help with certain risk factors related to heart attacks and strokes.
Even if it does benefit things like that, there is the major hurdle of the molecule size – it’s a chain made of 275 amino acids linked together. (5)
Our bodies break down proteins into individual amino acids before absorption, at least with the majority of large, complex proteins. This is the same argument made as to why Prevagen (apoaequorin) probably can’t be absorbed intact with oral consumption.
Remember, fibrinolytic drugs are given by IV. If nattokinase works, it can be hypothesized that intravenous administration may be the best delivery. Yet this all remains speculative, given how little human research there is so far.
Can you use nattokinase for cats and dogs?
Surprisingly, you will come across a number of conversations on forums and blogs about using a dosage for dogs and other pets.
There was a study published in 1990 in which thrombosis was intentionally inflicted on the dogs (yes, very cruel) and after giving them nattokinase capsules (orally administered) their circulation returned to normal after 5 hours.
Promising, yet without further studies, it’s premature to know if it can help your pet. (6)
Dr. Karen Becker, a veterinarian, developed a pet supplement containing nattokinase, ginger root, and ginseng. The packaging says it’s to “promote mental balance, alertness and vitality” and it’s aimed at older dogs and cats, as evidenced by the name; Geriatrics Solution Bites. It contains a 45 mg/serving (max) dosage of nattokinase.
Health benefits clinically studied
1. Preventing thrombosis on long-haul flights
Published in 2003, this was the first randomized and controlled human clinical trial involving nattokinase.
- The dietary supplement Flite Tabs was used. It contains a 300 mg blend of nattokinase and Pycnogenol.
- 204 high-risk people participated.
- 101 were given Flite Tabs and 103 were given placebo.
- Before and after their flights, ultrasound scans were done on veins in their legs.
- Edema was comparable in both groups.
The results?
- In the Flight Tabs group, no deep vein thrombosis was seen and their edema was better versus placebo.
- In the placebo group, 5 people had DVT and 2 had superficial thrombosis.
Something to consider is that this supplement included the usage of Pycnogenol, which is a patented extract of French maritime pine bark (Pinus pinaster). It’s unknown as to what effect, if any, each ingredient had. (7)
Even though the results are encouraging, keep in mind it’s only one study and is not considered sufficient evidence that it can treat, cure, or prevent thrombosis, edema, or any other disease. It’s sold for use as a dietary supplement only.
You can buy Flite Tabs on Amazon though consulting your doctor prior to usage is advised.
2. Lowering blood pressure
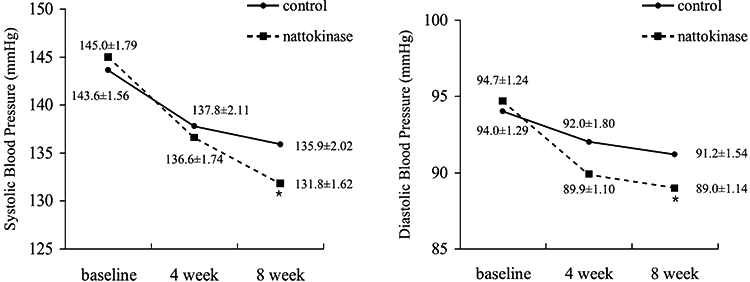
A university in South Korea conducted a randomized, double-blind, and placebo controlled trial to measure potential benefits for blood pressure.
- 86 men and women participated who had stage 1 hypertension, as defined by systolic blood pressure of 130 to 159 mmHg.
- Ages ranged from 20 to 80 years old.
- 44 of the people received a 2,000 FU (Fibrinolysis Units) dosage of nattokinase capsules, taken once per day for 8 weeks. The other 42 were given a placebo.
The results?
- 73 out of the 86 finished/complied with the trial protocol.
- When comparing the supplement vs. placebo participants, there was an average decrease of 10.5 points for systolic and 2.8 points for diastolic blood pressure.
- There was also a 1.17 ng/mL/h decrease in plasma renin activity (PRA) which plays a role in the body’s regulation of blood pressure, thirst, and urine output.
No adverse reactions were listed. (8)
3. Lowering cholesterol and blood lipids
Upon reading supplement reviews and commentaries, you often come across people taking or recommending nattokinase plus CoQ10, red rice yeast, ginkgo biloba, or another ingredient believed to support cardiovascular health. Do combos like these work synergistically or do they create contraindications?
Taiwanese scientists wanted to measure what happens when nattokinase and red rice yeast are taken together. Published in 2009, this trial was registered with ClinicalTrials.gov. (9)
- Randomized, double-blind, and placebo controlled.
- 47 patients participated who had hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol and triglycerides).
- They were split into three treatment groups; (1) 50 mg capsules of nattokinase, (2) 50 mg of nattokinase plus 300 mg of red rice yeast, and (3) placebo.
- The average ages for each group were in the 50’s.
- Each group took 2 capsules twice daily for a total of 6 months.
The results?
- In the nattokinase group, triglycerides decreased by 26% and the good HDL cholesterol increased by 8.9%. However after analyzing these compared to placebo, the results were not statistically significant.
- In the red rice yeast and nattokinase combined treatment group, there were significant decreases observed; 15% lower triglycerides, 25% lower total cholesterol, and 41% lower LDL cholesterol (which is the bad kind).
Nattokinase benefits for cholesterol and triglycerides might exist, but the changes seen in this study are too trivial to count. Only the combined usage with red rice yeast had statistically significant results. Without a separate group for just the yeast, it’s impossible to know if these beneficial effects were synergistic or solely coming from the yeast.
4. Improving risk factors for blood clots and CVD
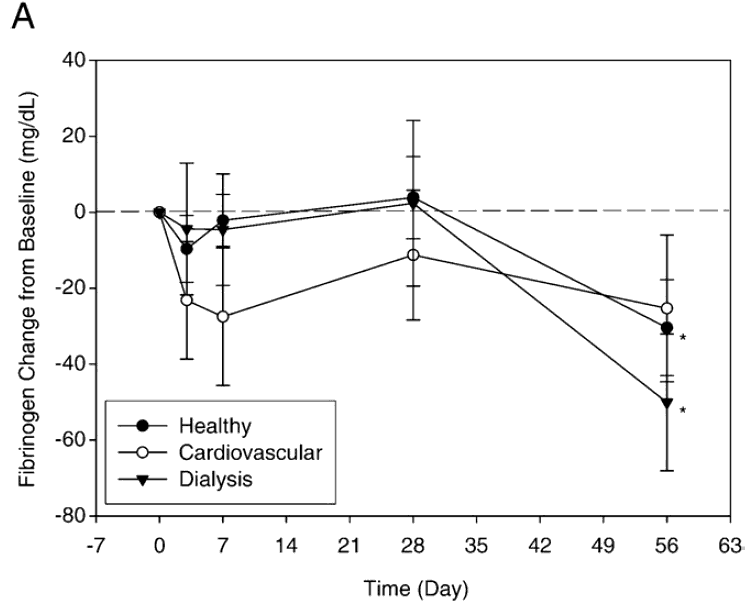
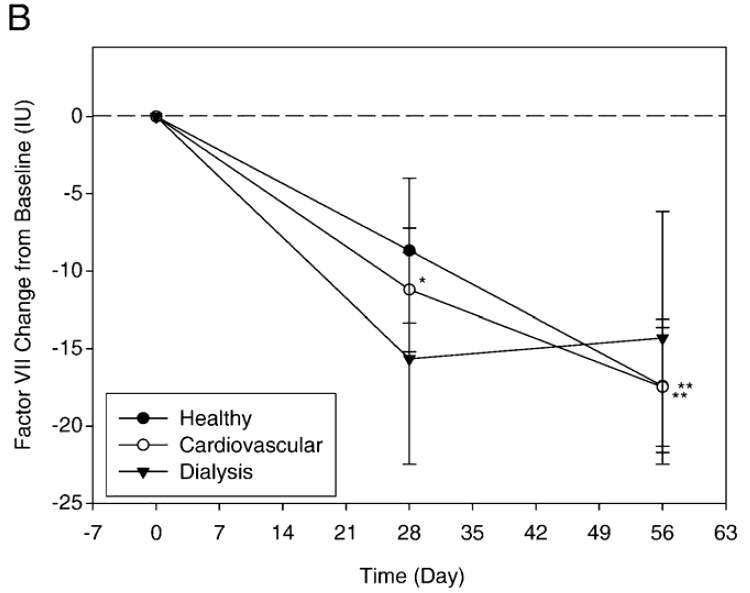
Taiwanese scientists also published this clinical trial in 2009. They wanted to see if it could reduce risk factors associated with blood clots and lipids associated with cardiovascular disease (CVD).
- Open-label and self-controlled design, with no placebo group.
- 45 men and women participated.
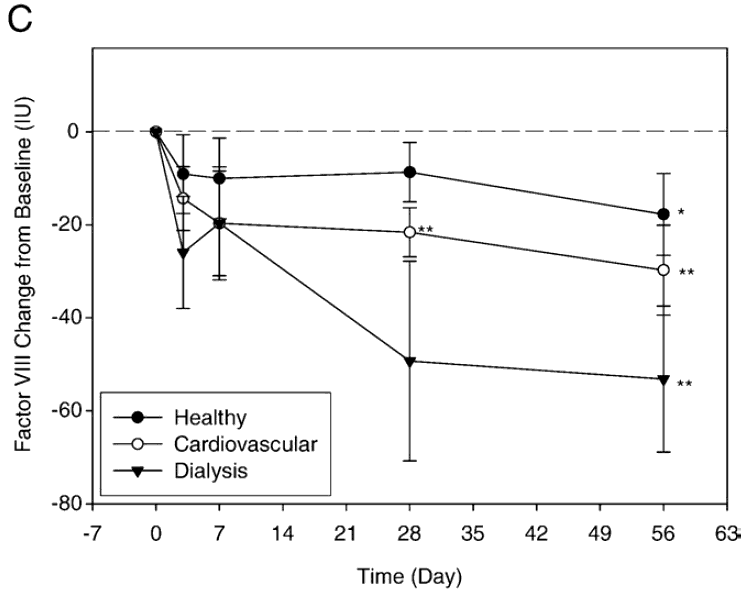
- They were split into three groups; (1) 15 in the “healthy group”, (2) 15 in the “cardiovascular group” who had cardiovascular risk factors, and (3) 15 in the “dialysis group” who were currently getting dialysis treatments.
- All groups received the same dosage; 2 capsules of nattokinase (4,000 Fibrinolytic Units total) taken once per day for 2 months.
The results?
In all 3 groups, there were lower blood levels detected of:
- Fibrinogen, which is a protein made by the liver that promotes blood clotting.
- Factor VII, which is a serine protease class enzyme that causes blood to clot.
- Factor VIII, also known as anti-hemophilic factor (AHF), is an essential blood-clotting protein.
These charts show how much of a decrease was measured in each group.
Soybean protein is linked to increasing plasma levels of uric acid. Normally uric acid is eliminated by the kidneys and when it builds up, it can cause gout and kidney damage.
This potential side effects was of particular concern for the dialysis patients. At least in this study, nattokinase kidney function influence was not seen according to uric acid levels, which remained stable throughout the study. (10)
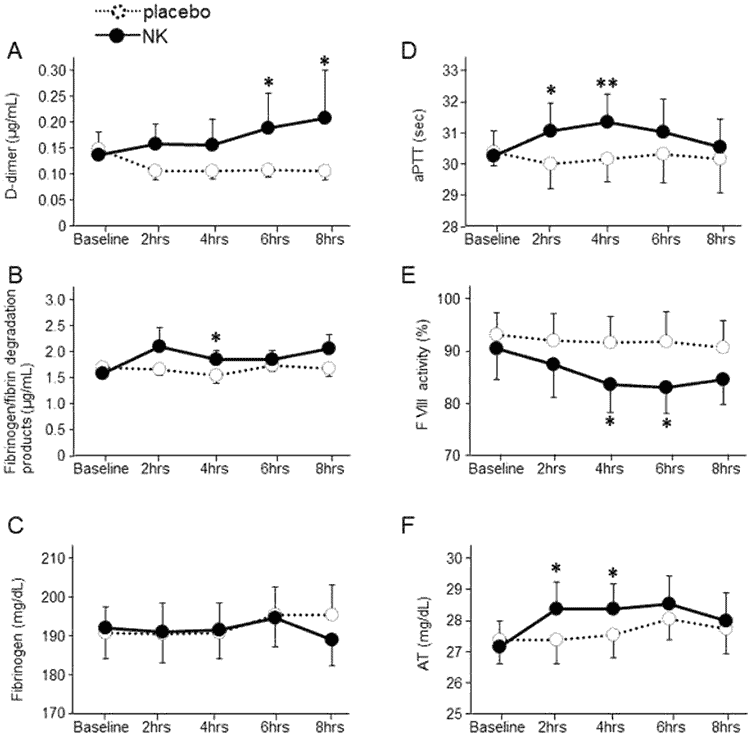
5. Altering blood factors after a single dose
Published in 2015, this is the most recent clinical study. While the others looked at using nattokinase long term, for weeks and months, with this one they wanted to see what would happen with a single dose.
- Double-blind and placebo-controlled
- 12 healthy young men participated, who averaged 22 years old.
- None had a medical history of hematologic (blood) or arterial diseases.
- None had used a nattokinase supplement previously and they stopped eating natto during the 2 months before the trial.
- Half the men were given a single softgel capsule containing 2,000 Fibrinolytic Units, while the other half received a placebo.
These were perfectly healthy young men of normal body weight and metabolic parameters. They did not have high blood pressure, cholesterol, or a history of deep vein thrombosis, blood clots, etc. Obviously they’re not at risk for a heart attack anytime soon.
For those reasons, to call the changes beneficial would be wrong. However if these same changes were happening in high-risk individuals, then they might very well be beneficial.
No side effects of nattokinase were declared, as the changes fibrinolysis/coagulation and blood parameters were considered to be within normal range.
Their conclusion states things well:
“In conclusion, a single-dose of NK [nattokinase] intake could be a useful fibrinolytic/anticoagulant agent to reduce the risk of thrombosis in humans. Further studies on NK are required to determine the details of metabolism, effective dosage and frequency, and safety for human use. Moreover, human trials demonstrating the clinical benefits of this action are limited, with no outcome data is available currently regarding this agent as an alternative to tPA, aspirin, warfarin, or newer anticoagulants.”
That last statement is worth reiterating. No one knows what type of drug interactions might occur with Coumadin, Plavix, Xarelto, or even aspirin. How long for nattokinase to dissolve blood clot, if it even works, has never been measured in a human. There are so many unknowns, which means its safety and efficacy as a potential treatment cannot be determined at this time. (11)
Other research (and lack thereof)
The following do not qualify as clinical trials according to PubMed’s classification system. Most are only lab research involving animals and cultured cells.
Nasal inflammation and mucus with asthma
Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps were studied using human tissue samples. When exposed to NK, they shrunk through fibrin degradation and the viscosity of their discharge (mucus) was improved in the treated tissue samples taken from asthma patients. (12)
Cognition and Alzheimer’s disease
Metabolites from fermented soybeans were tested in a rat model where cognition was impaired. Among the metabolites, there was nattokinase and K2 MK7, as well as the phytoestrogens daidzin, genistin, and glycitin. They appeared to offer a neuroprotective effect “through potent antioxidant activity” and showed inhibitory activity for amyloid-ß and BACE1, which are two markers for a brain with Alzheimer’s. (13)
Other research has also suggested it has “amyloid-degrading ability”. (14)
Atherosclerosis
Celiac disease and gluten intolerance
Research from Boston University reports that nattokinase appears to be a promising gluten-degrading enzyme. Of course, merely some degradation is not acceptable for Celiacs and those with moderate to severe gluten allergies. However those with a mild intolerance might experience better digestion by taking nattokinase supplements prior to meals containing wheat, barley, or other sources of gluten. (16)
Headaches
Using nattokinase for headaches and migraines is occasionally blogged about but it’s not backed by any published study.
A human study using a 4-week course of a natto-derived supplement did report improvements for shoulder stiffness, lower back pain, and coldness of the extremities, but “no significant difference was found in the VAS score for headache.” (17)
Skin and hair benefits
People who report using nattokinase for keloids, hair loss, and other forms of skin care and hair health are doing so based on no published data. You won’t even find the word “hair” or “skin” associated with it among the 27,000,000 entries in PubMed.
Nattokinase side effects
- Increased risk of bleeding
- Increased risk of bruising
- Potential interactions with blood thinners/anticoagulants (e.g. Coumadin, warfarin) and antiplatelet medicines (e.g. aspirin, Plavix)
- Increased risk of rupturing a brain blood clot, whose existence may be unknown
- Usage before surgery may increase risk of complications and lengthen recovery
- Unknown safety during pregnancy
- Unknown safety while breastfeeding
This list of adverse reactions should not be considered complete. With such limited data published, the potential side effects, drug interactions, and contraindications are unknown.
Even though soybeans are high in phytoestrogens, it’s highly unlikely there is a nattokinase estrogen influence. For starters, the dosages used are very little and what is being consumed is primarily a byproduct of the fermentation.
Some manufacturers infer they are safe for those with soy allergies, because testing reports they have less than 2 parts per million (ppm) of soy remaining. They are almost soy-free.
How to take
It is not a medicine. It should only be used as a dietary supplement, not for any disease or health condition.
Nattokinase dosages are reported two different ways; measured in milligrams and fibrinolytic units (FU). The most common dosages sold for each are 2,000 FU and 100 mg. Using either of those 1-3 times daily is what’s typically reported on the labels of major supplement brands.
Serrapeptase is a chemical that comes from the silkworm. Taking serrapeptase and nattokinase is a popular enzyme combination. Solaray makes it and the dosage they list is 3,000 FU of NK and 60,000 units of serrapeptase.
Is nattokinase safe?
For healthy individuals without blood irregularities and/or cardiovascular disease, its usage is generally well-tolerated. It is difficult to locate reviews or testimonials of users reporting gas, bloating, upset stomach, or any other side effects of probiotics and enzymes that are common.
Nattokinase overdoses have not been documented in case literature, so it’s unknown as to whether higher amounts are safe. This is why you should stay within the dosing instructions provided by the manufacturer. Consult your medical doctor before using.
Should you take nattokinase with or without food?
There are conflicting opinions on this. The brand Source Naturals says you should take 1 capsule 3x daily on an empty stomach with an 8 oz glass of water. Others report the best time to take nattokinase is prior to eating each meal. Some say twice daily, upon waking and again prior to bed, is the best dosing regimen.
There is not sufficient evidence to support any time of the day is better than another. Since it’s unknown as to whether it’s fat or water-soluble, saying it can work with food or with water on an empty stomach are all speculative opinions.
Supplement reviews
Most of the big brands sell it including Doctor’s Best, Enzymedica, Healthy Origins, Jarrow Formulas, NOW Foods, Pure Encapsulations, and Source Naturals.
However, just like with the ubiquinol form of CoQ10, these brands are not actually making it themselves. Most nattokinase is made in Japan (or at least by Japanese-owned companies) as the following three are who control most of the patents related to its production:
- Contek Life Science Co., Ltd
- Daiwa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd
- Japan Bio Science Laboratory Co., Ltd
That last one on the list owns the patents for Nattokinase NSK-SD, which has the vitamin K2 removed. For regular daily users that may be a good idea. Vitamin K of all forms, including K1, K2 MK-4, and K2 MK-7, are fat-soluble, so you can overdose on them.
You will find NSK-SD sold by Pure Encapsulations on Amazon. The brand Source Naturals and some generic/lesser-known names also offer it.
Aside from the differentiating benefit that NSK-SD offers, the best or highest quality nattokinase is subjective. The effects of gastric acid on it are unknown, but some prefer enteric coated nattokinase. Solaray sells vegetarian capsules that are enteric coated.
Not to say the other brands aren’t, but you will clearly see labeling that says non-GMO, vegan, and gluten free on Doctor’s Best veggie capsules.
If you want to buy raw organic nattokinase, the food source of natto may be your only option. The closest we are aware of is the USDA certified organic supplement by Pure Synergy. It’s not raw though and in addition to the 55mg (1,000 FU) of NK, there are other added plant extracts believed to be beneficial. You can get Pure Synergy Heart Protector on Amazon.
Because this remains a niche dietary supplement, it can be hard to find at CVS, Costco, Walmart, GNC, and other mainstream stores.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.