[toc]
Some people appreciate lambs’ quarter for its beneficial properties and effects, while others swear at the slightest mention of it, because they are allergic to it, besides the fact that the weed is difficult to deal with. This miracle plant, which has been around for a long time and is practically everywhere and grows where and when it wants, is considered a weed but has three main characteristics that give it the name “magic weed”. “Allergic/Toxic/Medicinal” – It blooms from June to even October. and its pollen season is June. Allergy is a tricky disease and worst than that it still hasn’t been fully researched. This is made more complicated by the fact that every year there are more and more chemical allergens, pollen is often displaced by air pollution and financial subsidies for research are scarce, so it is impossible to find the perfect cure. Allergic persons, therefore, try to cope on their own by looking for all-natural and effective ways to combat allergies.
Allergy sufferers’ immune systems become overzealous and start treating harmless substances, such as grass pollens or food particles, that enter the body every day as intruders. These are called sensitizers or allergens.
Once an allergen enters the body for the first time, which is managed by a hypersensitive immune system, the immune cells begin to produce IgE antibodies unnecessarily.
In turn, these antibodies leave a small unit on guard when the battle with the enemy is over – they attach themselves to so-called mast cells, which produce histamine (which normally fights infection). The first battle with the allergen is not accompanied by any discomfort. But the subsequent ones are a battle.
Your body recognizes the allergen, reminds itself that it has already fought against it, produces IgE antibodies, and transfers these to the mast cells to make them secrete large amounts of histamine. This in turn triggers a variety of defensive reactions in the form of symptoms, such as cough, runny nose, diarrhea, colic, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, rashes, etc.
It Is Not So Allergic But Still…
Its pollen concentration does not reach high values. Sensitization to lambs’ quarter pollen has been observed, but rarely with high severity.
With relatively low exposure, it is difficult to establish the clinical relevance of findings such as positive skin test reactions with lambs’ quarter pollen allergens or high levels of specific IgE class antibodies directed against this weed allergen.
The low maximum concentrations observed in urban areas where measurement points are located also suggest that low exposure to lambs’ quarter pollen allergens may translate into the low clinical relevance of pollen allergens of this plant.
Pollen Counts Of Lambs Quarter
Although lambs quarter (Chenopodium album L.) doesn’t cause severe allergic symptoms. It is worth avoiding, especially in June when it has its pollen season. It is an annual weed with leaves resembling the shape of a goosefoot (hence the Latin name Chenopodium; Chen = goose, podos = foot) belonging to the family of the mosquito or amaranthus.
Lambs quarter was also used in folk medicine. The plant still has many supporters today. The problem is that not all parts of lambs quarter are healthy and have medicinal effects. The flowers of lambs quarter bloom and pollen for a long time – from June until October. Its pollen is very volatile, and since it is an extremely common weed at pollen time there is just a lot of it.
Almost everything is known about the effects of pollen on the respiratory system – rhinitis, blocked nose, headaches, conjunctivitis, and, in the worst case, asthma.
Symptoms Of Allergy To Lambs Quarter
The lambs quarter blooms for a long time: from the end of July to the beginning of October, so people who are allergic to lambs quarter pollen can be uncomfortable for quite a long time.
Lambs quarter pollen is very volatile, but the concentration is usually not high, so it is rare for people to have a strong reaction to lambs quarter pollen
People who are allergic to lambs quarter pollen usually have symptoms such as runny nose, blocked nose feeling, headache, itchy eyes, conjunctivitis. Rarely, asthma occurs.
Lamb’s quarter dust is much loved by bees (it is an excellent source of protein for them), so people who are allergic to lambs quarter pollen are not recommended to eat honey harvested in late summer.
Additional symptoms
Anyone who has even a slight problem with lambs’ quarter pollen knows these symptoms very well. There is another problem, actually even two. The first concerns those who know the medicinal properties of the plant and consume it. Quite common in this case is sun allergy with quite unpleasant consequences – swelling of the skin, discoloration, or *diarrhea*.
The second problem stems from the fact that lambs’ quarter pollen is very much liked by bees, for whom it is an excellent source of protein. So if you have an allergy you should avoid honey too, or just hide it in a safe place so the bees don’t spread the lambs quarter.
Lambs Quarter And Allergy
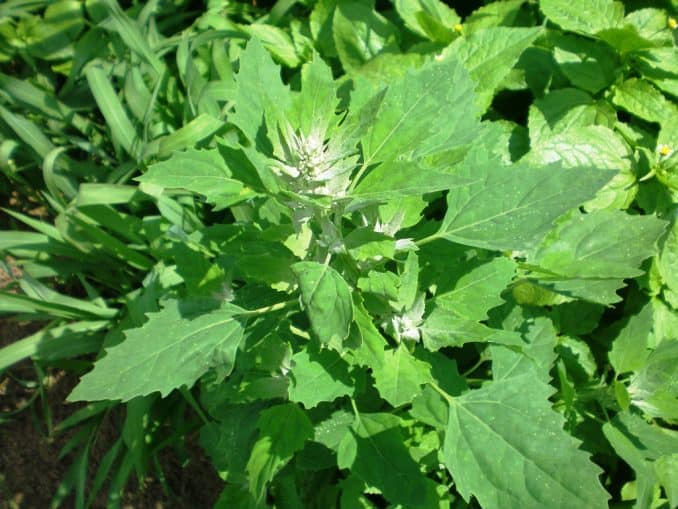
It is a wind-flowering plant, which typically grows to a height of about 0.1-1.5 m, and in rare cases to 3-3.5 m. The stem of this plant is simple, smooth, variegated in nature colors (green, red, or purple), with grooves along its length.
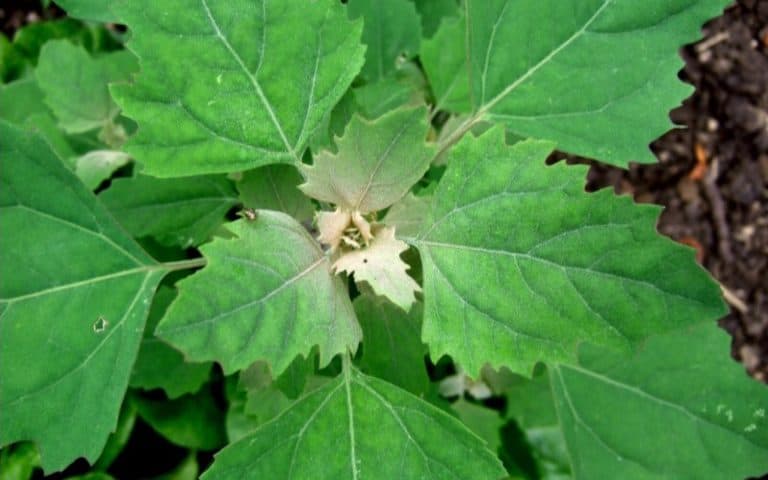
Leaves are wide, triangular, or rhombic, approximately 15 cm long, with an irregular serrated edge and white scales on the leaves, especially below the surface.
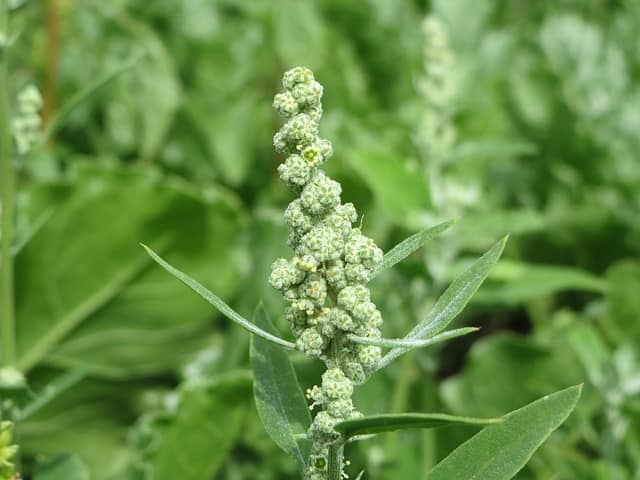
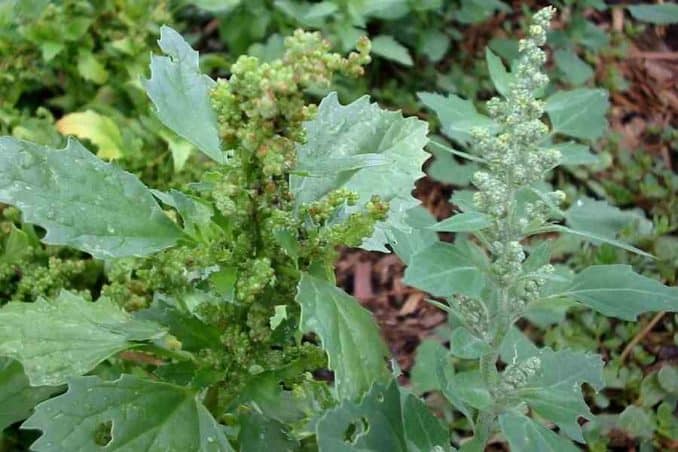
Leaves of young plants are oval with the opposite arrangement; with maturity, they leave space in alternate arrangement and become purple with white granules. The flowers are dioecious (hermaphrodite), green (without petals), formed in dense clusters. The seeds of this plant are reported to be small, disc or arch-shaped with a diameter of about 1.5 mm. This plant can produce about 20,000 pollen grains in one season
This plant is a popular choice for people suffering from celiac disease, however, it is important to mention that it is also a plant that can cause allergies. It is popular mainly among people suffering from celiac disease, however, it should be mentioned that lambs quarter is a plant that can cause allergy.
However, you should do an allergy test before consuming it for the first time because there is a risk of this plant causing anaphylactic shock.
- Conditions: allergic rhinitis; allergic asthma; allergic conjunctivitis.
- Symptoms: itchy, blocked nose or runny nose; postnasal drip; sneezing; itchy, red, or watery eyes; asthmatic symptoms.
Lambs Quarter As It Looks
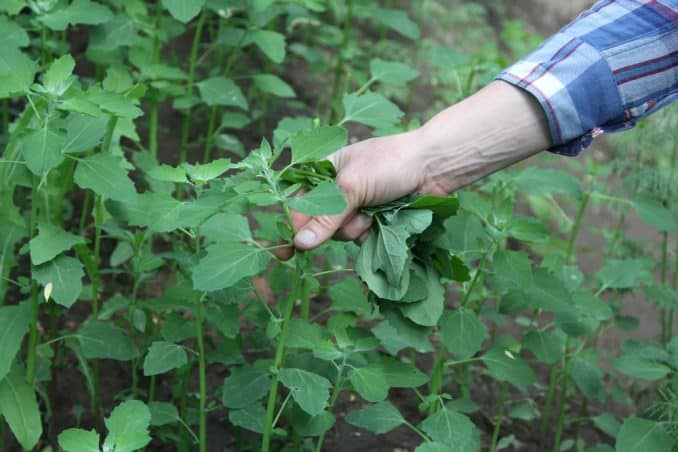
It looks so unassuming that it is often unnoticed or even destroyed by people passing by. The lambs quarter, as it is referred to, is commonly known as lambs quarter.
lamb’s quarter is light green and is covered with a light, slightly silvery mess – which is where the second part of its name in the plant classification comes from.
lambs quarter grows from a few centimeters up to about 1 meter tall. It is self-seeding and the wind disperses its seeds very easily. lambs quarter blooms from June to as late as October.
Where Does It Occur?
It’s a real cosmopolitan. It’s a common weed with almost 250 species and subspecies. About 25 species. You can find it on all continents and many islands. It grows in meadows, gardens, and fields.
Farmers treat this weed as either a nuisance or salvation. The lambs quarter is used in beet crops as a trap for aphids, which like to lay their eggs in it. Lambs quarter is said to be a ruderal plant, i.e.
it also grows in urban areas (e.g. between sidewalk slabs), polluted, post-industrial areas, rubble heaps, or roadside ditches. lambs’ quarter is very expansive – it robs other plants of water and nutrients, making it impossible for them to grow.
This species includes at least one variety (or subspecies) native to North America and one or more introduced varieties (or subspecies).
Lambs Quarter In Traditional Medicine
Lambs quarter, popularly known as lambs quarter is admittedly a common weed that is often found in your yard as well as your neighbor’s, but in times of poverty, it was the one that helped those who could not afford food survive hunger.
Related to lambs quarters is amaranth, one of the oldest food crops. Along with corn, potato, and beans, food amaranth was a staple crop of the Incas and Aztecs. Today again amaranth is used as a raw material for gluten-free groats. The pollen grains of amaranth have allergenic properties.
Beneficial Properties
Young leaves of lambs quarter were fried and served with potatoes, and its seeds were used to bake the so-called hunger bread. lambs quarter has many nutritional values, but not all of them.
Historically it has been used in herbal medicine – specifically its root and leaves. Externally applied to wounds, it soothed coughs and helped treat bronchitis.
Today, those who know its properties use it in cooking. The young leaves are prepared like spinach. They contain protein, carbohydrates, vitamin C, and provitamin A.
The seeds can be used to make flour and groats. However, one must be very careful, because older leaves and seeds are poisonous.
From an old medicine cabinet
Lambs quarter also shows medicinal properties. It contains in its composition provitamin A, vitamins B1, B2, C, carbohydrates, protein. Herbalists, aware of the fact that the plant can be a poison, however, knew who to recommend lambs quarter to.
Tinctures with it in their composition were recommended to people suffering from bronchi, chronic cough, and bronchitis. The poultices from the lamb’s quarters were also used for hard-to-heal wounds. Currently, it is not used in herbal medicine.
Life Cycle
An annual spring species. A single individual produces up to several tens of thousands of seeds (on average several hundred – several thousand). The seeds can easily survive in the soil for about 40 years. In the 60s of the last century, a case was described when during archaeological excavations live seeds of Lambs Sprouting takes place at temperatures between 5 and 33 ºC (best at 18 ºC – research conducted in the Czech Republic).
After passing through the digestive tract of horses, cows, and pigs, the ability to germinate was retained by 2.5; 16.29 and 20.36% of lambs quarter seeds, respectively. It is estimated that seeds of this species eaten by migratory waterfowl can be carried over distances of up to almost 3,000 kilometers
Applications Of Lambs Quarter
Due to its composition, rich in nutritional value, lambs quarter has many uses. Thanks to the high amount of green pigment – chlorophyll – it detoxifies the body, binds toxins, and excretes them from the body via the urinary system.
The protein and fiber content of the vegetable aids weight loss and increases metabolism. In your diet, it is worth combining lamb’s quarter with meat and leguminous vegetables.
It is a source of many nutrients
- fiber,
- carbohydrates,
- vitamins A, B, C, K,
- proteins,
- minerals: phosphorus, potassium, iron, calcium, and zinc.
Lambs quarter can be a good alternative as an ingredient in vegetarian and vegan diets because it contains large amounts of fiber and plant proteins. It is gluten-free, which is important information for people suffering from celiac disease. People with lactose intolerance will be pleased to know that it contains twice the amount of calcium as other plants.
Lambs quarter also contains antioxidants that slow down the natural aging process. Regular consumption of lambs quarter also affects the appearance of the skin. It has a strengthening effect on nails and hair and affects the work of growth hormone, which is invaluable for children. However, remember to exercise extreme caution in the use of lambs quarter Uncontrolled intake of the herb can cause serious health problems.
Lambs Quarter Toxic Effects
Despite its ability to help people survive in times of hunger and poverty, lamb’s quarter has toxic effects. Above all, older specimens of the plant should be avoided as they are more dangerous than the young plant, and its seeds should be properly heat-treated.
Symptoms of poisoning include malaise, fluctuations in blood pressure, diarrhea, and even convulsions. Allergic reactions in allergic individuals are also dangerous. Consuming lambs quarter in excess can also result in poisoning. especially on the skin. This is why the seeds must be thoroughly rinsed first. To ensure that the lambs quarter does not turn out to be a poison, you must also boil its seeds
Poisonous parts and their effects
Older leaves and seeds of lambs quarter are dangerous to our health. They contain dangerous saponins, oxalic acid, alkaloids, oleanolic acid. Additionally, the lambs quarter has a lot of nitrates in it, which it picks up from over-nitrogenized soils.
- Ailments that may occur after eating lambs quarter are:
- malaise
- diarrhea
- high blood pressure
- convulsions
- allergic reactions – severe skin redness and swelling – in people who have eaten lambs quarter and then spent a long time in the sun
Lambs in animals
This plant causes among horses, among others, swallowing and coordination disorders and even collapse, and in sheep and cows, among others, bleeding from the mouth, nostrils, and anus.
Lambs Quarter Medicinal Properties Herb
In the centuries since, lambs’ quarter was one of the ingredients of people’s food, associated with poverty and hunger. Today it is sometimes used as an ingredient in medicinal concoctions. The plant has another property: it is poisonous. For this reason, it should not be consumed without consulting a person with knowledge of botany.
Lambs quarter is not popular in modern medicine and only a few people know about its medicinal properties. It is treated as a weed and removed from home gardens. lambs quarter owes its medicinal properties to its young leaves and seeds, which are used in cooking and unconventional medicine.
Medicinal Properties
In traditional medicine, preparations of lambs quarter were used as an agent:
- disinfectant – especially for urinary tract infections and urolithiasis,
- decongestant for colds, flu, bronchitis, asthma, and tuberculosis
- supporting the rehabilitation of eyesight defects – nearsightedness, farsightedness,
- calming – e.g. in the treatment of neurosis,
- cleansing the body from toxins,
- and as a poultice for abrasions, burns, and skin inflammations.
Nowadays, lambs quarter is no longer used in herbal medicine, but it still has its supporters among lovers of natural methods of treatment and body support.
Study Doesn’t Lie
According to research, lamb’s quarter has an antibiotic effect and fights microorganisms such as Staphylococcus aureus, as well as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
The phytoalexin content influences muscle regeneration after a workout or other effort, and also supports the immune system, improving resistance to all kinds of infections.
Importantly, lambs quarter provides more potassium than tomatoes alone, as much as 288 mg per 100 g of heat-treated lambs quarter. This element is great for preventing hypertension and supporting the work of the circulatory system. It reduces the level of bad cholesterol, which prevents atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease.
Lambs quarter use in cooking
The young leaves (up to about 15 cm in size) of lambs quarter and its young seeds are used for culinary purposes. To make sure they are safe for us to eat, the concerns of the ingredients need to be heat treated. The leaves have to be boiled or scalded with boiling water and then thoroughly rinsed.
The seeds, on the other hand, need to soak overnight in water with lemon juice, then boil, and carefully pour off the cooking water. Young leaves of lambs quarter are handled the same way as spinach. They can be added to salads, scrambled eggs, pancakes, pasta, soups, and dry cakes. The seeds can be used to make porridge or flour.
History Of Lambs Quarter
In the past, lamb’s quarter was used as an ingredient in health tinctures to prevent many ailments. They cured chronic cough, inflammation of the upper respiratory tract, and bronchitis. Decoctions made based on lambs quarterzalek were recommended for colds and flu.
They improved metabolism as they had a cleansing effect. They were also used to make poultices for hard-to-heal wounds and ulcers. The root and the herb were used in herbal medicine as raw materials for the products mentioned above, however, these treatments are not practiced nowadays
It is interesting to note that it even grows in cold Greenland and Spitsbergen. The only place where it does not occur is Antarctica, as the ambient temperatures are far too low even for this plant.
Seed longevity
An annual plant that is wind-pollinated and produces many seeds that have an enormous lifespan. They can burrow deep enough into the soil not to germinate – in this way they can survive for up to 3,000 years.
Soil that appears to be free of weeds is often overgrown after harrowing, digging, or even deeper raking. This is because the mechanical treatment has pulled the hidden lambs’ quarter seeds to the top, causing them to spread across the meadow or garden.
It was Indian tribes who made lamb’s quarter famous as a plant that could be used as a meal. lambs quarter is called lambs quarter, but it is not the same as lambs quarter. The latter is otherwise known as oregano or wild marjoram.
Lambs quarter for whom?
It finds its place on the plate, in fact, for everyone who appreciates health, ease of preparation of meals, and unusual solutions. It will prove useful as an addition to the diet of:
- children – it enhances the production of growth hormone and is a source of protein,
- celiac patients – it does not contain gluten,
- vegans and vegetarians – high content of vegetable protein replaces meat products in the diet,
- physically active people – grains can be an ingredient of a high-protein meal after training or hard physical work,
- lactose intolerant – lambs quarter contains twice as much calcium as milk alone,
- obese – dietary fiber supports digestive function,
- diabetics – lambs quarter has a low glycemic index, so it is also safe for people with insulin resistance,
- people suffering from atherosclerosis and hypertension – high potassium content regulates the functioning of the circulatory system.
Damage Caused By Lambs Quarter White As A Pest
Lambs quarter is appreciated by nutritionists, but it is also a weed. This means that once it spreads, it can be difficult to eradicate. Especially since it grows very well in a variety of soils and produces extremely hardy seeds.
Unfortunately, lambs quarter as a weed, when it dominates a given space, results in lower than normal vegetable yields, especially for beets and corn.
Lambs quarter competes strongly for nutrients. It takes up large amounts of nitrogen and water from the soil, so it can cause significant yield losses.
Adaptation
The lambs quarter quickly adapts to new environments, and its seeds that rest in the soil for years can seriously threaten a new crop. Lambs quarter should be controlled as soon as possible, as soon as seedlings appear.
Just a small amount of it (the damage threshold in corn is 0.5 units/square meter, and for beets, it is 1 unit/square meter) is enough to reduce yield quality and quantity. Because lambs quarter weed is a host for plant pests and a host for some types of fungi, it is necessary to take action as early as possible to eliminate this plant from crops.
How To Protect Yourself From Lambs Quarter?
When growing crops in the field, we can use what is called night plowing. Many agricultural experts believe that night plowing can reduce weeds in the crop. If weeds are not exposed to light, they do not have the opportunity to grow well.
Although this method will probably not exclude the use of chemical spraying, it is worth experimenting with because it carries no risk. On large plantations, we avoid frequent fertilization with nitrogen. lambs quarter very much likes this component, so it is more likely to grow on soils rich in this element.
How to protect against lambs quarter weed in the garden?
- On beds intended for cultivation or not used lay black agro-fiber. Soil not settled by any plants will have time to regenerate. Weeds will not grow out of it, because agro textile cut off their access to light. If you do not plan to grow crops for a long time, mulch can be covered with bark, which will enhance the appearance of the garden.
- In addition to mulching with nonwoven fabric, try mulching with compost, straw, or natural fertilizer.
- Weed the beds regularly (by hand or by hoeing). Weeds should be pulled out when the soil is moist. Then it is easiest to remove them in one piece.
- Destroy uprooted weeds by burning them. Do not deposit them on compost or store them in containers. Immediately after pulling out the noxious plants, put them in a bucket and carry them out of the growing area.