[toc]No, its scientific name of Hippophae rhamnoides has nothing to do with hippos, but it does with horses. Here’s the Latin to English translation for each part:
hippos = horse
phae (phaos) = light
Horselight?! The grammatically correct translation is giving light to a horse. The meaning of its name came from the earliest recorded use – in ancient Greece, they reportedly fed the berries to horses to make their fur glossier. Eye benefits for the horses were also claimed, which might be a 2nd reason that phaos was chosen (in ancient times, “light” was synonymous with eyes and their ability to see). (1)
This plant is one of the hardiest berries on earth.
These tiny orange fruits can be found growing at high elevations, ranging from 4,000 to 12,000 feet above sea level (1200 to 4500 meters).
Despite its name, the sea buckthorn does not grow next to the ocean, nor is it related to buckthorns (Rhamnaceae family).
You often find them thriving next to river banks and being that they’re drought tolerant, they also grow on the sunny sides of steep slopes. Soil with high levels of salt and acidity is no problem for the plant, either.
With the exception of North America, its native habitat is the sub-arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere. This includes Russia, Europe, and Central Asia. Today they are also cultivated in North America, but primarily in Canada and not the US.
Other names it goes by are seaberry, sandthorn, and sallowthorn.
What is sea buckthorn oil?
Not be confused with an essential oil, this is an edible extract which is rich in the essential fatty acids as well as phospholipids, phytosterols, carotenoids, and vitamin E.
Since the berries have 12x the vitamin C content of oranges, the oil may also be a source of that depending on how it’s processed.
For skin care uses and as a dietary supplement, the oil is more popular than berry powder and the fresh fruit. Organic, cold-pressed, and supercritical CO2-extracted oils will best preserve these phytonutrients.
Seed vs. berry oil

Sea buckthorn seed oil is the most common. It has an almost perfect 1:1 ratio of omega 3 (linolenic acids) and omega 6 (linoleic acid) at 34% and 32% respectively.
It’s also the best source of the other fat soluble nutrients in the plant such as vitamin E and the various carotenoids. Quercetin and kaempherol, two anti-inflammatory and antioxidant compounds, are also prevalent in the seeds. (2)
Sea buckthorn berry oil is made by pressing the flesh of the fruit. Being that vitamin C is water soluble, it’s primarily found in the fruit which is why this form will contain greater amounts of C.
Its drawbacks is that less of the fatty acids will be present, which is why calling it a fruit oil is a bit of a misnomer, since it mainly consists of the water.
Essential fatty acids (EFAs) like omega 3 & 6 are different than a plant’s essential oils. Those are volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and they’re not fixed or stable fats, like the EFAs. Although it’s possible to make sea buckthorn essential oil, no one sells it because for this particular plant, you would be removing the most beneficial components.
Whether it’s the oil made from the seeds or the oily juice from the berries, watch out because many products dilute these with other fats, such as olive oil. With juices, they can even be advertised legally as “100% juice” if it’s only diluted with water.
To get the best of both worlds, many brands of oil will combine both the seed and fruit.

When it comes to skin care – like face creams and body lotions – some are made from the the seed extract while others use the berry. Both provide naturally moisturizing fats for your skin, but the seed will provide more.
Softgels or capsules will typically stick with the seed oil. You will most often see them marketed as omega 7 supplements (palmitoleic acid) because this plant is the best food source.
Omega 7 is the rarest fatty acid. Even cold water fish like salmon contain very little.
Macadamia oil is the next best source of omega 7. However given the high calories and other fats in this nut, the most practical way get that nut in your diet may be to switch from almond to macadamia milk.
Fresh sea buckthorn berries
If you live in the United States, it’s virtually impossible to find fresh buckthorn fruit for sale. Not a single commercial berry grower in the entire country sells them. The plant’s preference for high altitudes and cold climates doesn’t lend itself well to most of the country, even if there was demand for them.
That lack of demand for fresh is ultimately why no one grows it. Health benefits aside, there’s a good reason for that…
What does fresh sea buckthorn taste like?

Like a sour orange or pineapple. They are very tart and bitter with almost no sweetness. The whole fruit is very watery, which makes it messy to eat relative to other berries. When dried, the sour flavor is so concentrated that many consider them to be unpalatable for eating.
The low sugar (fructose) content is good for diabetics, but bad for you if you’re expecting buckthorn berries to taste like a dessert.
The smell of sea buckthorn is hard to agree on. Tangerine may be the closet fruit to compare it to. The oil smells like wet wood.
Not the most pleasant thing in the world, but it’s not disgusting either. Because the scent is so subtle, it’s really a moot point.
Given the characteristics of its taste and smell, you can understand why almost no one sells these berries fresh.
Whether it be California (Superfoodly’s HQ), the northern neighbors of Oregon and Washington, or the Midwest and East Coast, we haven’t heard of the berries being sold at any farmers market. Some Canadian farmers do sell it though, such as Vale Farms in Lumby, British Columbia. The Healing Arc’s Golden Orchard was the first in Ontario to grow and sell them to the public.
Wherever you live in the United States, you can buy fresh sea buckhorn online which have been frozen. The photo above is what they look like after thawing.
Northwest Wild Foods sells these but they’re not cheap at $40 per 3 pound bag. Since they have to be shipped with dry ice, there’s another $15 shipping charge if you’re in the Western states, or $30 for elsewhere in the country. There’s no promo code for free shipping, but if you spend $125+ you can get it waived.
We bought the dried and frozen sea buckthorn berries for the purpose of this review, but given their flavor and expense, let’s just say it will be our first and last order!
The health benefits of sea buckthorn
The following characteristics have been observed in studies involving humans, animals, and/or cultured cells when treated with the fruit, the oil, or other forms of extract:
- Skin anti aging through the quenching of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
- Skin sunburn and UV damage reduction
- Tear secretion in patients with dry eyes being increased
- Cataract progression being delayed
- LDL cholesterol and triglycerides lowering
- Liver protective effects
- Anti-diabetic effects seen in glucose and insulin responses
- Anti-cancer activity observed in cultured cells
- Neuroprotective effects seen in aged mice and rats with brain injuries
To reiterate, this list of advantages if only theoretical and all remain unproven. For any given benefit, not a great deal of clinical research exists. (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13)
You will see hair products like shampoo, conditioner, and serum make use of the oil. Even though its namesake comes from its purported ability to boost the sheen of coats and manes on horses, using sea buckthorn oil for hair growth or follicle strength has not been researched. Though it has been for gastric ulcers in horses and was said to benefit those. (14)
Which benefits have the best evidence?
Antioxidants are prevalent in many plants and the ORAC value of these berries is only moderate, so that in and of itself is hardly a reason to pay up.
By far the most impressive and unique thing about sea buckthorn is its omega 7 content. Very few people are aware of just how rare this essential fatty acid is in nature. To put it in perspective, here are the top 10 food sources and how much each contains.
| Foods Highest In Omega 7 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Food | Percentage By Weight | Mg Per 100 Grams of Food |
| 1. | Sea buckthorn oil | 24% | 24,000 |
| 2. | Macadamia nuts | 15% | 15,000 |
| 3. | Whale blubber | 6.8% | 6,800 |
| 4. | Anglerfish liver | 3.9% | 3,900 |
| 5. | Lard | 2.3% | 2,300 |
| 6. | Baker’s yeast | 1.7% | 1,700 |
| 7. | Japanese eel (Kabayaki-style) | 1.4% | 1,400 |
| 8. | Butter | 1.2% | 1,200 |
| 9. | Pacific herring | 1% | 1,000 |
| 10. | Salmon cavier | <1% | 950 |
| Sources: (15) (16) | |||
It’s 60% more than the next contender, macadamia nuts. Obviously you’re not going to be eating whale blubber anytime soon. Pigging out on a plate of lard would have disastrous consequences, for the health of your heart as well as your waist line. Plus, lard has over 90% less omega 7. With butter, it’s 95% lower. When you compare it to the other highest sources, you understand why the seaberry oil is in a league of its own.
The research suggests that the most compelling and more unique beneficial effects the plant may have are coming from this particular fat.
Since omega 7 is a fat, the most potent source of it will be the oil. The whole fruit and juices will contain mostly water-based components.
They remain unproven for now, but what follows are the three most compelling reasons to supplement with the oil.
Beautiful skin
It’s too expensive of an ingredient for drugstore face creams, but a number of premium and specialty skin care brands make use of it. You probably already know that, but what you may not know is that this plant appears to be effective from the inside out, too.
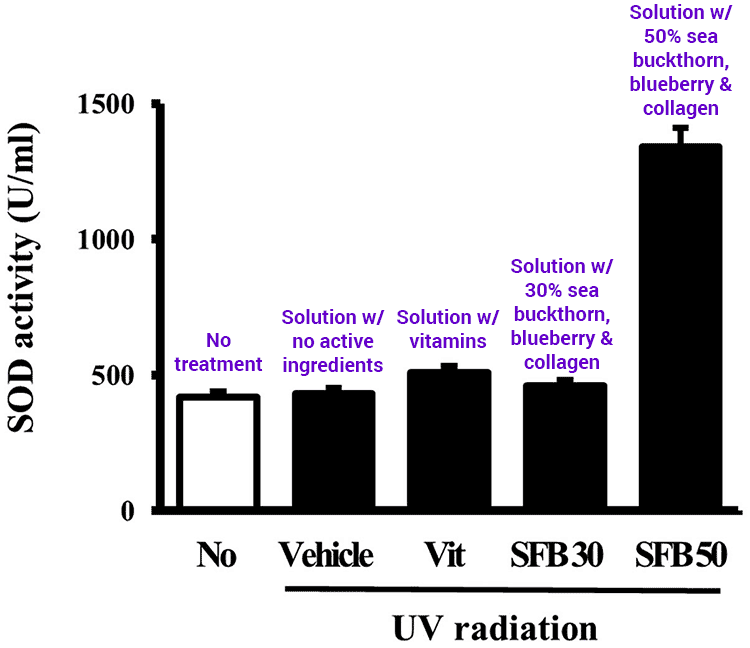
Wrinkles, texture, and pigmentation were measured in a study involving hairless mice. They were exposed to UV radiation for 6 weeks. During that time, half of them were given an oral dosage formula consisting of sea buckthorn extract (31.4%), blueberry extract (25.4%), and collagen (8.3%). (17)
For those mice treated with the highest strength of this formula (SFB50) the results were impressive…
In both humans and mice, superoxide dismutase (SOD) is a potent antioxidant we internally produce. For the mice given the supplement, their SOD production was “increased dramatically.” Nearly 150% more than when only vitamins were given to them.
Levels of skin wrinkling, dermal thickness, moisture, and collagen-1 expression all benefited.
Many people talk of using sea buckthorn capsules for acne rosacea and atopic eczema, however those uses have not been studied. (18)
Something no one talks about which has been studied is vaginal atrophy – the thinning and drying of the vaginal mucous membrane that’s common post menopause. A total of 116 postmenopausal women were given the oil capsules in a 3 gram daily dose or a placebo version. (19)
“Compared to placebo, there was a significantly better rate of improvement in the integrity of vaginal epithelium in the SB group…”
When the oil is applied topically, some research suggests it may help burn wounds, atopic dermatitis, and possibly too much sebum being secreted during acne vulgaris. (20) (21) (22) (23)
The problem with most products…
…is that they use only a low percentage of the oil. Even some of the $80+ anti-aging serums on the market list it far down on their ingredients list. The throw a little in the bottle for marketing, but really you’re only getting a trivial amount.
One solution we like is to buy sea buckthorn oil and by using the dropper, you can mix some in with your normal anti aging face cream. Add it to the jar of cream directly, or in the palm of your hand during each application. For 100% pure and cold pressed organic oil, try a bottle of Poppy Austin available on Amazon.
Dry eyes

As published in The Journal of Nutrition, a double-blind and randomized trial was conducted with 100 women and men who suffer from dry eye and its associated side effects. (24)
- 52 were given a daily dosage of sea buckthorn oil equal to 2 grams.
- 48 were given a placebo version made of palm kernel and coconut oil that looked the same.
- To control the dosages, both groups received them in the form of capsules.
- They used them for 3 straight months, during fall and winter months.
“The results of this study suggest that SB [sea buckthorn] oil consumption can attenuate the increase in tear film osmolarity occurring during the cold season. It may also influence the maximum intensity of redness and burning symptoms in participants with dry eye. Contact lens wearers reported fewer overall eye symptom days in the SB group.”
So why does the oil of sea buckthorn seem to help with dry eyes and blepharitis?
The omega 7 fat might not be the reason. A study out of Finland concluded that it appears to be the carotenoids and tocopherols in the oil that benefit eye inflammation in the meibomian gland cells. Though it still could be omega 7, because they also said that eicosanoids (signaling molecules) might be produced by these fatty acids. (25)
Which form works best? A study using mice claims that the berry oil (not the seed oil) is what seems to restore tear production values best. (26)
The brand EuroPharma sells a dietary supplement blend of the berry pulp and seed oil which has been clinically studied for dry eyes due to weather, computer use, and aging. They’re marketed under the name Terry Naturally softgels.
Liver health

Aflatoxins are dangerous fungi which can infect crops, especially peanuts since they grow underground. They are known to increase the rate of liver cancer in both animals and humans. (27)
Chickens were administered aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) in a study. When they were simultaneously given a sea buckthorn oil supplement, it was found their liver histology “showed a significant reduction of necrosis and fatty formation compared with chickens treated with AFB1 alone.” The amount of poison residue in their livers was “significantly reduced.” (28)
As you can imagine, conducting human trials like this are next to impossible, since no one in their right mind will voluntarily allow for a known carcinogen to be given to them!
However there is a human trial out of Shanghai which involved 48 patients who already had cirrhosis (liver disease). (29)
- 30 people were given a large dosage of sea buckthorn extract – 3x per day of 15 grams.
- 18 people were instead treated with a vitamin B complex – 3x per day.
- Each group took these daily for 6 months.
Those treated with the oil were said to have improved serum levels of laminin, total bile acid (TBA), hyaluronic acid, collagen types III and IV. Their conclusion was it…
“…may be a hopeful drug for prevention and treatment of liver fibrosis.”
Sea buckthorn oil side effects
One tablespoon of pure oil weighs 14 grams (14,000 mg). Since most supplemental dosages are only 2 to 3 grams (2,000 to 3,000 mg), it’s too trivial of an amount per day to cause any weight gain. Some people do experience side effects but they are uncommon with the typical dosage size:
- Reduced blood clotting
- Lowering of blood pressure
- Yellowing of skin
- Diarrhea
- Unknown pregnancy safety
With the yellowing of skin, that was from a single case study of a 45 year-old man who had consumed high amounts of sea buckthorn berries (the entire fruit) for 6 months. It was not from using the purified oil. (30)
There’s no reason to believe using sea buckthorn while pregnant or breastfeeding is dangerous, but on the flip side, there’s no certain way to say it’s safe since those scenarios haven’t been studied.
The changes in blood pressure and blood flow is based on data from studies suggesting that might be happening. For people with certain diseases, those otherwise beneficial changes could be adverse reactions instead.
Verdict?
This superfood is in a class of its own when it comes to omega 7. Nothing else – whether plant, fish, or animal derived – comes remotely close to its content.
Is sea buckthorn good for your skin? Whether it’s for fighting UV damage, wrinkles, or other signs of aging, the research for these and other benefits is still quite early. Likewise for heart, liver, and eye health. You can’t claim any of these things are proven, but the science so far suggests these berries and the oil extract might be good for you in multiple ways.
 Where to buy sea buckthorn oil?
Where to buy sea buckthorn oil?
Online will be your best bet. We checked Whole Foods (Los Angeles) and while they carried a $30+ pasteurized juice supplement, there were no capsules or pure oils for sale. Disappointing but not surprising, as they don’t carry the main vegan omega 3 brands, either.
You will probably strike out at places like Target and Walmart, too. Not all, but many of the supplement brands that CVS and Walgreens peddle are lower end and made in questionable countries like China.
Being a blend of both seed and berry oils, we love Seabuck Wonders softgels on Amazon. For topical skin care, try their organic berry oil.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.


 These tiny orange fruits can be found growing at high elevations, ranging from 4,000 to 12,000 feet above sea level (1200 to 4500 meters).
These tiny orange fruits can be found growing at high elevations, ranging from 4,000 to 12,000 feet above sea level (1200 to 4500 meters).
 Where to buy sea buckthorn oil?
Where to buy sea buckthorn oil?