Your immune system is a complex network that defends against disease, but it doesn’t function at its peak on its own. Enhancing it requires precise knowledge and targeted action, not mere guesswork or generalized advice. With misinformation rampant, finding trustworthy methods to bolster your immune defenses is essential.
[toc]
This guide presents the top 10 scientifically-backed ways to boost your immune system. From diet and exercise to understanding your unique physiological needs, we will navigate the proven strategies for immune support. These aren’t quick fixes or marketing gimmicks; these are actionable insights grounded in research, ready for you to apply.
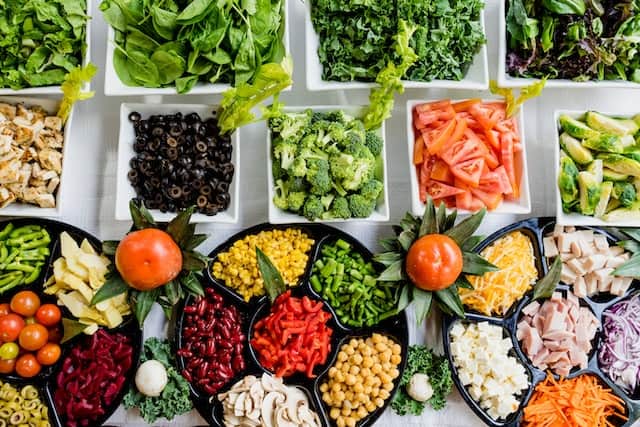
1. Balanced Diet: The Foundation of a Healthy Immune System
Fruits and Vegetables
Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits and vegetables are essential for the immune system. A study by the Harvard School of Public Health emphasizes their importance in immune support, particularly Vitamin C and Vitamin E. Including a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables ensures a broader spectrum of nutrients.
Proteins
Proteins play a crucial role in the body’s defense mechanism. Foods like fish, chicken, and beans provide amino acids that are vital for immune cell production. Ensuring a proper balance of protein sources can optimize immune function.
Healthy Fats
Healthy fats like omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil help control inflammation. A study conducted by the Journal of Clinical Investigation showed that these fats might improve immune response. Incorporating these fats in your daily diet may contribute to overall immune health.
Water Intake
Proper hydration supports overall health, including the immune system. Drinking enough water helps in the production of lymph, which carries white blood cells and other immune system cells. Staying hydrated is an easy and effective way to support immunity.
- Oranges and strawberries for Vitamin C
- Almonds for Vitamin E
- Salmon for omega-3 fatty acids
- Chicken for protein
- Water for hydration
2. Exercise: A Vital Contributor to Immune Health
Regular Physical Activity
Regular exercise improves circulation and contributes to general good health. According to a 2019 study published in the Journal of Sport and Health Science, it may enhance the immune response by promoting healthy turnover of immune cells. Creating a consistent exercise routine tailored to your fitness level can be beneficial.
Intensity of Exercise
While regular exercise is beneficial, overly intense exercise can have adverse effects. Balancing the intensity ensures the immune system isn’t compromised, according to research by the American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine. Listening to your body and not overdoing exercise is key.
Outdoor Exercise
Exercising outdoors may provide added benefits such as increased Vitamin D production, which has been linked to immunity in several studies including a 2017 review in the Journal of the American Osteopathic Association. Fresh air and natural sunlight can enhance these benefits.
3. Sleep: Recharging the Immune System
Quality of Sleep
The importance of sleep in immunity is widely recognized. A study by the Archives of Internal Medicine showed that those who sleep less may be more prone to infections. Quality sleep is essential for a robust immune response. Establishing a regular sleep routine may facilitate better sleep quality.
Duration of Sleep
Adults need 7-8 hours of sleep for optimal function. Consistent sleep supports the body’s ability to fight off infections. Setting a consistent sleep schedule may help in achieving the required amount of restful sleep.
Sleep Disorders
Addressing sleep disorders is vital for immune function. Disorders like insomnia can hinder the body’s natural defense mechanisms. Consulting a healthcare provider for chronic sleep issues can lead to tailored solutions.
4. Stress Management: An Unseen Barrier to Immunity
Understanding Stress
Chronic stress can suppress immune function. A study published in the Journal of Immunology Research showed that stress hormones could inhibit the immune response. Learning individual triggers and how to manage them is essential.
Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness practices such as meditation and yoga can reduce stress. These practices have been associated with enhanced immune function in research, including a 2016 study in the Journal of Behavioral Medicine. Incorporating mindfulness into your daily routine can foster long-term benefits.
Professional Help
If stress becomes unmanageable, seeking professional help is essential. Therapists can provide personalized strategies to manage stress effectively. Don’t hesitate to seek support if needed, as mental well-being significantly affects immunity.
5. Avoiding Harmful Substances: Keep Toxins at Bay
Tobacco
Smoking cigarettes is known to weaken the immune system. A study in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology has outlined the negative impact on immune cells. Quitting smoking can be a significant step towards enhancing immunity.
Excessive Alcohol
Excessive alcohol can impair the immune system. Moderate consumption is key, as outlined in a study by the journal Alcohol Research. Responsible drinking is part of a lifestyle that supports immune health.
Recreational Drugs
Recreational drugs can have various negative effects on the immune system. Awareness and avoidance are essential to maintaining a healthy immune response. Education about the potential risks can help in making informed decisions.
6. Regular Medical Check-ups: Early Detection and Prevention
Regular Screenings
Screenings can detect problems before they become serious. Early detection can help in taking timely action to boost immunity. Keeping up with recommended screenings is proactive health management.
Vaccinations
Vaccinations are an essential part of preventive healthcare. They work by stimulating the immune system to fight specific diseases, as supported by extensive research. Keeping vaccinations up to date is an effective prevention strategy.
Consulting with Health Professionals
Regular consultations with healthcare providers ensure that individual health needs are addressed, including those related to immune health. Open communication with healthcare providers enables personalized care.
7. Herbal and Nutritional Supplements: A Complementary Approach
Understanding Supplements
Some herbal and nutritional supplements may support immune health. However, it’s essential to consult with healthcare providers, as not all supplements are beneficial or suitable for everyone. Transparency about supplements with your healthcare provider ensures safe use.
Evidence-Based Supplements
Using evidence-based supplements ensures that the products are supported by scientific research. Supplements like zinc and Vitamin D have been studied for their potential immune-boosting effects. Using supplements backed by research ensures credibility and efficacy.
Quality of Supplements
The quality of supplements can vary widely. Choosing high-quality products that meet regulatory standards is crucial. Look for certifications and consult with healthcare providers to choose quality supplements.
8. Hygiene Practices: The First Line of Defense
Hand Washing
Hand washing is one of the most effective ways to prevent the spread of germs. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasizes its importance. Regular and thorough hand washing using soap and water can significantly reduce the risk of infections.
Food Safety
Proper food handling prevents foodborne illnesses. Following guidelines from regulatory authorities ensures that food is prepared and stored safely. Being diligent in food preparation practices can prevent potential health risks.
Avoiding Close Contact with Sick Individuals
Avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick can reduce the risk of contracting illnesses. If caring for a sick individual, taking precautions like wearing a mask can minimize exposure. Such measures are essential in maintaining your immune defense.
9. Individual Needs: Personalizing Immune Support
Age Considerations
Immune function changes with age, and strategies must be tailored accordingly. Children, adults, and seniors may have different immune needs. Understanding these needs and adapting lifestyle practices is crucial.
Chronic Conditions
People with chronic conditions may have specific immune challenges. Tailored strategies are essential for enhancing immune function in such cases. Collaboration with healthcare providers can create individualized plans.
Genetic Factors
Genetics can play a role in immune function. Personalized medicine and genetic counseling can provide insights into individual immune system needs. Embracing the potential of personalized medicine can lead to more targeted and effective solutions.
10. Debunking Myths and Understanding Limitations
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Myths about boosting the immune system are prevalent. It’s essential to differentiate between scientifically supported practices and misinformation. Educating oneself through reliable sources is key to avoiding misconceptions.
Recognizing Limitations
Not all methods will work for everyone. Recognizing the limitations of certain practices and focusing on a holistic approach is key. Being open to adjustments and flexibility can enhance your personalized immune-boosting journey.
Counterarguments and Critical Thinking
Some may argue that immune boosting is a marketing gimmick. Critical thinking and referring to research can help in understanding what truly works. Engaging with credible research and critical evaluation ensures an approach grounded in evidence and reality.
Conclusion
The journey to fortify your immune system is neither simple nor one-size-fits-all. It’s a nuanced interplay of diet, physical activity, rest, mental well-being, hygiene, personalized considerations, and an understanding of what’s factual versus what’s fictional. This guide provided you with ten research-backed, actionable strategies to uplift your immunity. No magic bullets or empty promises, just solid science tailored to meet individual needs.
The path to a more robust immune system is clear and within reach. Now it’s up to you to take these evidence-based steps and make them a part of your daily life, fostering a healthier, more resilient you.