Heart health is pivotal at every stage of life. The right exercises not only strengthen the heart but also enhance overall well-being, regardless of age. This guide delves into the top heart-healthy exercises designed for all ages, emphasizing practicality, accessibility, and effectiveness.
Let’s embark on a journey to a healthier heart through exercise, backed by science and tailored for everyone from children to seniors.
Walking: The Universal Exercise
Accessibility for All Ages
Walking is a fundamental exercise that requires no special equipment and can be done anywhere. It’s particularly beneficial for beginners or those with mobility issues. Regular walking improves cardiovascular health, aiding in weight management and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Studies show that brisk walking can significantly lower the risk of heart disease and stroke. It’s an exercise that can be easily integrated into daily routines, making it sustainable long-term.
Variety and Flexibility
Incorporating different walking styles, such as speed walking or hiking, can add variety and challenge. These variations help engage different muscle groups and prevent boredom, making it more likely for individuals to stick with their exercise regimen.
Impact on Mental Health
Walking not only benefits physical health but also significantly impacts mental well-being. It has been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, contributing to a healthier heart by lowering stress levels.
Engaging in regular walks in nature has additional benefits, including improved mood and increased feelings of happiness and contentment.
Building a Routine
Starting with short distances and gradually increasing the time and intensity is key to building a sustainable walking routine. Setting realistic goals and tracking progress can motivate individuals to continue. For those with health concerns, consulting a doctor before starting any new exercise routine is crucial to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Scientific Backing
Research supports walking as an effective way to improve heart health. A study published in the American Heart Association’s journal highlights that walking at a moderate pace for at least 150 minutes a week can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.
Another study emphasizes the benefits of walking for reducing high blood pressure, a major risk factor for heart disease.
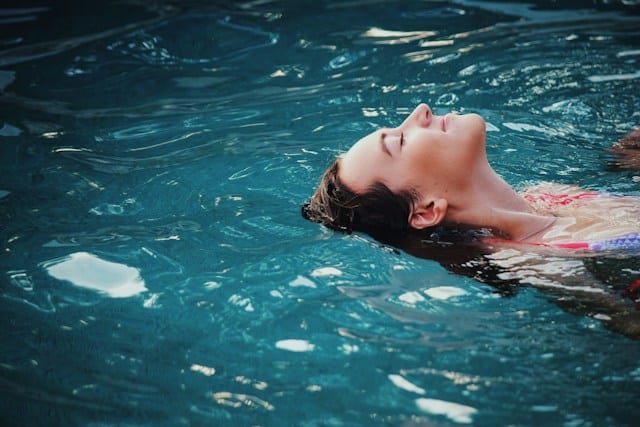
Swimming: Low-Impact Cardio
Benefits for Joint Health
Swimming is an excellent low-impact exercise, making it ideal for people with joint pain or arthritis. It allows for a full-body workout without putting stress on the joints, promoting heart health while protecting the body’s mobility.
This exercise strengthens the heart and lungs, improving cardiovascular endurance and efficiency.
Improving Muscle Tone and Strength
The resistance of water during swimming helps in toning muscles and building strength. Engaging multiple muscle groups simultaneously boosts heart function and circulation.
Regular swimming sessions can lead to significant improvements in muscle strength, endurance, and flexibility, contributing to overall heart health.
Stress Reduction and Mental Health
The rhythmic nature of swimming and the soothing effect of water can significantly reduce stress levels. This reduction in stress contributes to lowering blood pressure and improving heart health.
Swimming has also been linked to improved mental health, including reductions in anxiety and depression, further supporting cardiovascular wellness.
Variety of Strokes for Different Needs
Different swimming strokes offer varied levels of intensity and focus on different muscle groups. Alternating between strokes such as freestyle, breaststroke, and backstroke can enhance overall fitness and prevent workout monotony.
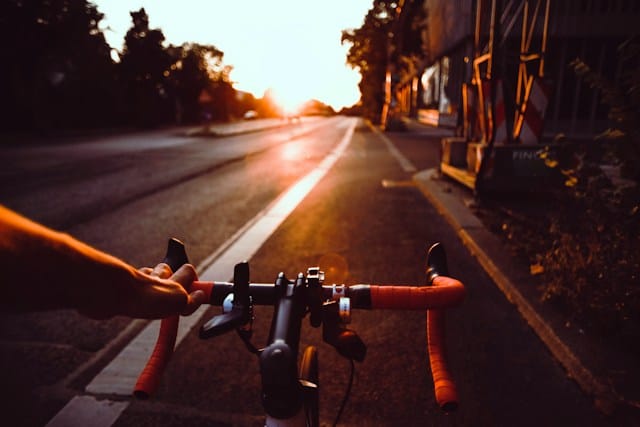
Cycling: Heart Health on Two Wheels
Cardiovascular Benefits
Cycling is another low-impact exercise that significantly benefits heart health. It helps lower blood pressure, reduce bad cholesterol, and improve blood sugar levels, all of which are critical factors in heart disease prevention.
Regular cycling strengthens the heart muscles, improves circulation, and increases lung capacity.
Indoor and Outdoor Flexibility
Whether it’s outdoor biking on trails or stationary cycling indoors, this exercise offers flexibility to fit any lifestyle. Indoor cycling classes provide a high-energy, community-driven environment, while outdoor cycling connects you with nature and offers fresh air and scenic views.
Both forms of cycling can be adjusted in intensity, making them suitable for all fitness levels and ages.
Weight Management
Cycling is an effective way to burn calories and manage weight, directly impacting heart health. Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on the heart and lowers the risk of heart disease.
Integrating cycling into daily routines, such as commuting or running errands, can make it an easy and practical part of a heart-healthy lifestyle.
Building Endurance
Over time, regular cycling can build physical endurance, enhancing the ability to perform activities with less fatigue. This increased endurance supports heart health by improving its efficiency and resilience. Gradually increasing the duration and intensity of cycling sessions can maximize these benefits.
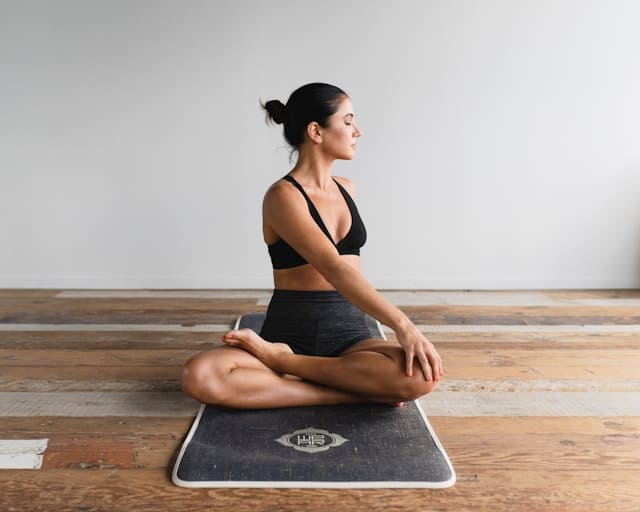
Yoga: Mind-Body Harmony
Stress Reduction and Heart Health
Yoga is renowned for its ability to reduce stress and promote relaxation, directly benefiting heart health. Techniques such as deep breathing and meditation can lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of heart disease.
Regular yoga practice has been linked to decreased levels of stress hormones, which are harmful to the heart.
Improving Flexibility and Circulation
Yoga poses (asanas) improve flexibility, balance, and strength, positively affecting cardiovascular health. Enhanced circulation from yoga practices ensures that the heart receives a steady supply of oxygen-rich blood, vital for its function.
Increased flexibility can also reduce the risk of injuries, making physical activity more accessible and enjoyable.
Heart Rate Variability (HRV)
Yoga has been shown to improve heart rate variability, an indicator of the heart’s ability to respond to stress. A higher HRV is associated with a healthier heart and a lower risk of cardiovascular disease.
This improvement in HRV highlights the interconnectedness of mental and physical health in promoting heart wellness.
Accessible to All Levels
Yoga offers various styles and intensities, making it accessible to beginners and advanced practitioners alike. Restorative yoga can be particularly beneficial for older adults or those with mobility issues, focusing on relaxation and gentle movement.
For more vigorous heart health benefits, styles like Vinyasa or Ashtanga can provide a more intense cardiovascular workout.
Community and Support
Participating in yoga classes provides a sense of community and support, enhancing the overall experience. The guidance of a knowledgeable instructor can ensure proper technique, maximizing the benefits for heart health.
Online classes and resources also make yoga accessible to those who prefer to practice at home, allowing for flexibility in one’s schedule and environment.
Strength Training: Beyond Muscle Building
Improving Cardiovascular Health
Strength training, often associated with muscle building, also offers significant benefits for heart health. It helps reduce body fat, lower blood pressure, and improve cholesterol levels.
Metabolic Benefits
By increasing muscle mass, strength training boosts metabolic rate, aiding in weight management and blood sugar control. These effects are crucial for maintaining a healthy heart, as obesity and diabetes are major risk factors for cardiovascular disease.
Regular strength training can improve insulin sensitivity, further protecting against heart disease.
Enhancing Endurance and Functionality
Building strength enhances overall physical endurance and functionality, making daily activities easier and less taxing on the heart. This increased capability encourages a more active lifestyle, further promoting heart health.
Strength training also improves balance and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and injuries, especially in older adults.
Scientific Support
Research supports the role of strength training in promoting heart health. Studies have found that moderate-intensity strength training is effective in reducing heart disease risk factors, comparable to the benefits of cardiovascular exercises.
Guidelines suggest incorporating strength training exercises at least two days a week for optimal heart health benefits.
Group Fitness Classes: The Motivational Boost
Enhanced Accountability and Motivation
Group fitness classes offer a unique environment that fosters accountability and motivation. Working out with others can push individuals to perform better and stick to their exercise goals, directly benefiting heart health.
The structured format of classes ensures a balanced workout, covering all aspects of fitness necessary for a healthy heart.
Variety and Fun
With a wide range of classes available, from aerobics to dance fitness, there’s something for everyone. This variety keeps exercise interesting and engaging, reducing the likelihood of boredom and dropout.
Fun and enjoyment are crucial components of a sustainable exercise routine, directly impacting heart health through consistent participation.
Accessibility for Beginners
Group fitness classes are designed to accommodate all fitness levels, with instructors often offering modifications for beginners or those with specific needs. This inclusivity ensures that everyone can benefit from the heart-health advantages of regular exercise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, incorporating a mix of cardiovascular, strength, and flexibility exercises into your routine is key to maintaining heart health at any age. Each of these top heart-healthy exercises offers unique benefits and can be adapted to fit individual needs and preferences.
By embracing a variety of activities, individuals can enjoy a comprehensive approach to heart health, backed by scientific evidence and designed for lifelong wellness.