[toc]After peanuts – which aren’t even a real nut – this one is the most common.
Sure, cashews have a deliciously nutty and creamy taste, but that’s not the only reason protein bars and superfood snacks often include them.
The biggest motive – for food manufacturers – is because they’re inexpensive. Compared to almonds, walnuts, and pistachios, they’re cheap.
In this case, cheap doesn’t mean bad.
Affordable, yet among the healthiest nuts you can buy regardless.
What are cashews good for?
Aside from their favorable nutrition facts like high protein and mineral content, this nut is being researched for depression, cholesterol lowering, Parkinson’s diseases, diabetes, and many other unexpected uses. Cashews make a great plant-based dairy-free alternative for making milk, yogurt, and cheese.
Let’s review all the ways they’re good for you, or potentially may be. Keep in mind that all of the following medical benefits discussed are preliminary and unproven. This food should not be used to treat, cure, or prevent any disease.
Cashew benefits
1. Tied for lowest calorie nut
A few years back, The Wonderful Company ran marketing campaigns for pistachios touting them as “lowest calorie” nut, without “the” in front of that phrase.
According to The Washington Post, the reason for the carefully crafted verbiage was really because they are among the lowest calorie. They are actually tied with cashews. (1)
With 160 calories per 1 oz serving, cashews slightly beat peanuts at 161 and almonds at 163 calories. Hazelnuts are 11% higher than cashews at 178, walnuts have 16% more at 185, and macadamia are most at 204 calories, which is 28% greater.
That’s according to the USDA National Nutrient Database. (2)
2. Lowest fat nut
What is the lowest calorie and lowest fat nut?
Cashews are tied with pistachio for calorie count, but they beat for total fat content. Per the USDA, 100g of raw cashews have 43.85g of fat, while pistachios have 45.32. Cashews are the lowest fat nut.
3. Weight loss
Lowest doesn’t mean low. As with all nuts, they’re still high in fat.
So how can such a calorically-dense food be good for losing weight?
The reason cashews are good for weight loss is two-fold. Multiple scientific studies have concluded that not all of the lipids (fats) in nuts are being absorbed during digestion. The other reason is because they offer greater satiability. They are hard and crunchy, which leads to chewing and taking longer to eat vs. potato chips and similar snack foods.
That extra time to eat them may not seem significant, but it is for appetite suppression. Even after you are full, it takes time for the nerves in your stomach to register that feeling.
The fact that not all of the fats are being absorbed is known as “the pistachio principle” but research suggests its applicable to all tree nuts, including cashews, almonds, and others.
There have been almost 20 clinical trials and not a single one has reported body weights that would be expected, if all of the calories were being absorbed. (3) (4)
4. Good source of BCAAs
Branched chain amino acids (BCAA) are three types of protein that your muscles need greater amounts of when recovering from strenuous exercise. Bodybuilders in particular benefit from supplementing with them.
| Branched Chain Amino Acids (BCAA) Per 100 Grams | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pistachios | Peanuts | Almonds | Cashews | Walnuts | |
| Leucine | 1600 mg | 1535 mg | 1461 mg | 1285 mg | 1170 mg |
| Isoleucine | 932 mg | 833 mg | 745 mg | 731 mg | 625 mg |
| Valine | 1262 mg | 993 mg | 848 mg | 1040 mg | 753 mg |
Even though cashews are not the highest protein nut, their amino acid profile packs a potent concentration of leucine, isoleucine, and valine.
5. Protein of 5.2g per ounce
Having 17% more, pistachios and almonds are the winners for total protein content.
Though consider how expensive raw shelled and organic pistachios can be. Almonds actually have less of the BCAA valine.
6. Low carb
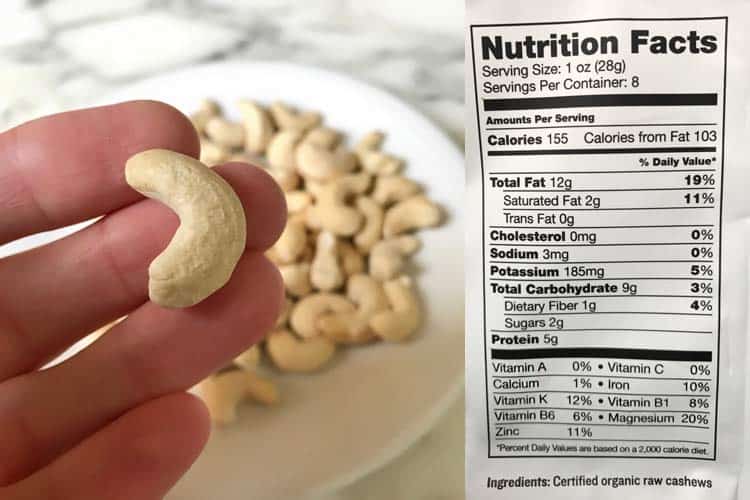
How many carbs there are in cashews is very low. Each ounce of nuts contains just 9g, which is 3% of the adult’s daily value. This makes them an ideal food for ketogenic and low carb diets.
7. Moderate magnesium, iron and zinc
Per ounce, cashews offer 10% of the daily value for iron, 11% for zinc, and 20% for magnesium.
8. Source of vitamin K
It’s not vitamin C, A, or E which are impressive. In fact, only trace amounts of those are present.
Raw organic cashews measure as having 12% of the daily value for vitamin K per ounce. That’s according to the nutritional label on Sunfood Superfood cashews. You can buy them on Amazon. Conventionally grown brands often report lower; 8% of the DV for vitamin K.
With the exception of pine nuts, no others offer you this essential vitamin, which plays an important role in blood clotting and for the binding of calcium in bones. (5)
9. Heart-healthy fats
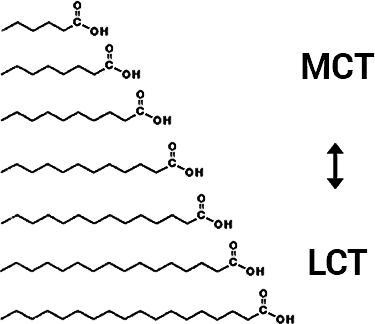
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCT) like lauric acid are in coconut. They are believed to be digested differently; through the liver via the portal vein. MCTs can provide quick energy like carbs, without spiking blood sugar. (6)
The long-chain saturated forms don’t offer this perk. Those are the types in cheese, meat, and other animal-based foods. They’re linked to an increased risk of heart disease and strokes. (7)
You won’t get saturated MCTs from nuts, but the good news is that they only have low amounts of the long-chain saturated.
The fat content in cashews is 18% saturated. 73% is in the form of monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which are healthier for your heart.
10. May lower LDL cholesterol
This is the type of cholesterol you want lower.
Published in 2017, a randomized and controlled human clinical trial looked at what happened to LDL cholesterol when 51 men and women ate cashews daily.
When compared to the control diet, their LDL decreased by nearly 5% after 28 days.
This beneficial effect is believed to be caused by the nuts monounsaturated fat. Those bind to dietary sources of cholesterol in the digestive tract, leading to you excreting rather than absorbing all of them. (8)
11. May lower blood pressure
Published in a 2018 issue of The Journal of Nutrition, a 12-week study was conducted where 129 people ate cashews every day, while another group of 140 did not. The daily amount was 30g, which is about 1 ounce.
Those eating the nuts experienced a decrease in systolic blood pressure of nearly 5 points. (9)
Now that study involved type 2 diabetics. What about everyone else?
A few years prior, a meta-analysis was published. It was a systematic review of numerous clinical trials which looked at nut consumption and blood pressure. It turns out that nuts in general correlated with lower systolic blood pressure, even in healthy individuals without type 2 diabetes. (10)
12. Consumption correlates with higher HDL
HDL cholesterol is the good kind that you don’t want decreased.
In that 2018 blood pressure trial, those eating cashew nuts also experienced a nearly 2 point boost in HDL.
13. Improves Parkinson’s model in mice
Published in 2018, a Brazilian university created a Parkinson’s model with mice, by using the pesticide rotenone to mimic the disease.
Next, they measured what happened to their locomotor activity, coordination, and spatial memory when they were treated daily with anacardic acids derived from cashew nuts.
The results were impressive; in a dose-dependent manner, the anacardic acids reduced the behavioral changes and oxidative stress caused by the Parkinson’s disease model. In part, this was due to their influence on mitochondria and superoxide dismutase (SOD) gene expression. (11)
SOD genes play an important role in fighting free radicals by internally producing antioxidants. (12)
14. Reduces brain injury in rats
Cerebral ischemia is a condition where there’s insufficient blood flow to the brain, which results in permanent brain damage.
In a rat model where ischemia was induced, there appeared to be a protective effect when they were pre-treated using a cashew-derived protein hydrolysate with high fiber.
In these charts, the “AO” is for the cashew treatment. You can see how as the dosage increased – from 2 to 50 mg – the damage in the cortex and striatum of thire brain decreased (lower bars). (13)
15. May help depression and sleep
Are cashew nuts good for depression?
If you search the PubMed database for tryptophan and depression, you will see over 300 clinical trials listed. There’s a lot of research pointing to this amino acid having mind-altering effects. Higher intake has been associated with better sleep, less anxiety, and fewer symptoms of depression. (14) (15)
The benefits of cashew nuts for depression have been greatly exaggerated. Claims that two handfuls contain enough tryptophan to rival the benefits of Prozac was an alternative medicine myth. It made the rounds on social media years ago. Snopes and others have debunked this. There isn’t even a cashew depression study that’s been done.
It is true that in 100g (3.5 oz) of raw cashews, there’s 320 mg of tryptophan. Whether that acts as natural antidepressant or anti-stress agent is yet to be determined. What can be said is that studies suggest this amino acid may help your mood in multiple ways. (16)
16. Useful for making vegan cheese
Is vegan cheese healthy? There are many lactose-free and dairy-free cheese brands on the market, but many are made using oil.
Daiya and Follow Your Heart may taste great when melted but they’re basically just refined oil, with little to no protein. Cholesterol-free but far from being a superfood.
For something closer to a whole food, cashew cheese is an excellent alternative. The nuts can be soaked and puréed to make a vegan cheese that also contains protein.
The best cashew cheese brands you can find at grocery stores are Miyoko’s Creamery, Parmela Creamery, Heidi Ho Organics, and Treeline. There are others but these are the brands with the widest distribution. Use them on pizza, tacos, grilled cheese, and any other food which normally uses dairy.
17. Creates a higher protein nut milk

Now you can find milks made with many types of nuts and seeds.
Cashew milk offers more protein than hemp milk and macadamia milk.
It’s a great plant-based beverage for those with soy allergies, or who simply want to minimize soy intake due to their phytoestrogens.
18. Used in cancer research
They are the most bizarre nut, no doubt.
The reason cashews are not sold in shells is because they are in the same family as poison ivy (Anacardiaceae). Their outer shell contains urushiol, the same skin irritant which causes extreme itching with poison ivy and oak.
The nuts of cashew grow on what’s called a false fruit, also known as an accessory fruit. The purpose of it is so that predators (animals) go for the “fruit” and forget about the seed, which is the only important part for the plant’s reproduction. With this species, the false fruit is often referred to as a cashew apple.
It’s not the edible seed kernel, but rather other parts of the plant which have been used in cancer research.
In 2017, academic research out of the United Kingdom reported that a compound called zoapatanolide A, which was isolated from cashew tree leaves, exhibits notable cytotoxic activity in the lab on cultured HeLa cancer cells. (17) (18)
That same year, a Chinese university tested cardanol monoene, which is the main phenolic compound in cashew shells. Using cultured human melanoma (skin cancer) cells, they found this compound to inhibit proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. (19)
19. Dogs can eat them
My dog ate a bag of cashews, what should I do?
Probably nothing. Truly raw cashews are dangerous to dogs and cats because they contain a toxin which requires high-heat like roasting to destroy. Cashews for dogs in small amounts are a healthy treat, however they pose a choking hazard since they don’t have the same molars as humans do for chewing and grinding nuts. To safely eat them, cashew butter mixed in with dog food may be the best method.
In Trinidad and Tobago, the bark of the cashew tree is used for the treatment of dog diarrhea as part of ethnoveterinary medicinal practices. It’s unknown if the nuts offer the same advantage. (20)
Side effects of cashew
The side effect you are most likely to experience when eating cashews is an allergic reaction. Being a tree nut, it’s among the top 8 allergens.
The Department of Allergy at Cambridge University in the UK reports that allergic reactions to cashew nuts are generally more severe than those experienced by peanut allergy sufferers. This was based on a comparison of 141 case studies in children with tree nut allergies. Side effects can include difficulty breathing, swollen throat, itchiness in the mouth and esophagus, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and anaphylaxis. (21)
Even for those not allergic, trace amounts of urushiol in the raw nuts may cause itchiness and similar reactions.
Food poisoning from salmonella-contaminated cashews has been reported by the FDA on multiple occasions. This danger is primarily shared with hazelnuts, macadamia, walnuts, and pine nuts. The risk of salmonella, along with traces of urushiol, are reasons why raw cashews are potentially less safe for you to eat. (22)
Mount Sinai Hospital in New York published a case study in 2016 of a 64 year-old man who experienced an autoimmune hepatitis reaction from eating large amounts of raw cashews daily or frequently. Diagnosis was based on a liver biopsy and enzyme measurements. (23)
Given the risk of bacterial poisoning, pregnant women and those who are breastfeeding should probably avoid eating raw cashews. Steam pasteurized will be safer, because food borne pathogens like salmonella will have been killed. Aside from that risk, there is no evidence to suggest cashews are dangerous during pregnancy, however they have not specifically been studied in pregnant humans or animals.
Eating cashews is not known to cause drug interactions. If you are on medications and plan on eating this nut regularly, consulting your doctor is advised because high-fat foods in general may affect the absorption of certain medicines.
The best types to buy
What are the best quality cashew nuts in the world?
Even if organic, the cheapest may not be the most ethically sourced.
Their hard outer shells are covered in cardol and anacardic acid, two caustic substances which can cause skin burns on the workers who harvest them. In India, where 60% of the world’s cashew supply comes from, many workers are not provided protective gloves. The conditions in Vietnam, another major exporter, have been claimed to be even worse. (24)
Ideally, you will want to buy brands of cashews which are fair-trade. Some USDA certified organic sources measure as having more vitamin K and other phytonutrients. If you want raw nuts, make sure they are from a trusted supplier since salmonella poisoning is a safety concern.
A popular and affordable brand on Amazon is Terrasoul Superfoods. Although not fair trade certified, they only source from growers paying fair wages and who protect their workers. Buy their 2 lb bulk bag of raw organic nuts. For a steamed version, try Sol Simple organic in a 6 oz bag which come from Nicaragua.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.