[toc]You know a food looks out of this world when it’s chosen for an episode of Star Trek and Star Wars: The Force Awakens.
They chose it because most people – or at least most moviegoers – have never seen one before.
Now that’s starting to change.
This exotic fruit is starting to show up in the produce section of grocery stores in the West.
What is a kiwano melon?
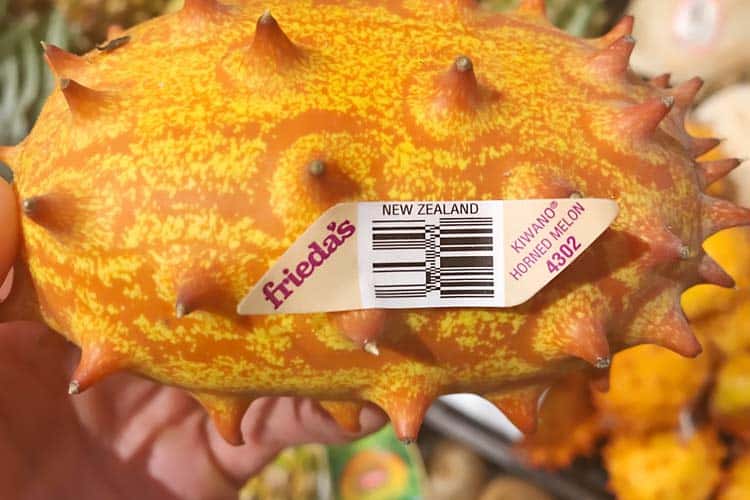
The kiwano comes from South and Central Africa. It’s in the same family as cucumbers and melons. Each fruit is around 5″ long and 3″ wide. Sharp but stout spines cover its thick yellow-orange skin. The pulp inside is a dirty lime green and contains hundreds of edible seeds.
Kiwano is a trademarked name which Frieda’s, Melissa’s, and a consortium of other brands use to market it. Outside of the US, UK, Australia, and New Zealand, the kiwano is more commonly known as an African horned melon or cucumber. Other names for it include jelly melon, melano, and hedged gourd.
Its scientific name is Cucumis metuliferus. Cucumis is in reference of the plant genus of cucumbers. The Latin word metuliferus means bearing (ferus) small pyramids (metula).
What type of fruit is a kiwano?
As part of the Cucumis genus, the kiwano is in the same family as cucumbers (Cucumis sativus), cantaloupe (Cucumis melo), and watermelon (Citrullus lanatus). Some call it a horned melon while others call it a horned cucumber. Since both are non-scientific culinary terms, it’s subjective as to whether you think of a kiwano as a cucumber or a melon.
What does it taste like?
The kiwano taste is very subtle. It’s often described as a cross between a regular cucumber and a zucchini. Some say it has the sweetness of a kiwi. When fully ripe, there’s also a hint of banana flavor.
The fruit’s texture on the tongue is a bit slimy, but not in a bad way. It’s like eating a partially puréed cucumber. The seeds are also similar, except there are more of them. Most people eat kiwano seeds because it’s too much work to pick them out. However, they don’t have much taste. You can’t really chew them either, as they just glide down your throat.
The saponins in horned cucumber cause it to be naturally foamy, even without agitation.
Can you eat the kiwano skin or peel? Most people don’t but it is edible. To eat it, you first have to use a vegetable peeler or knife to remove the spikes. After doing so, many Africans eat it like an apple with its skin – by simply biting into it.
Health benefits
The fruit, leaves, and root of the plant have been consumed in various parts of Africa for as long as historical records are available.
In the Okavango Delta region of Botswana they seldom use it as a food source, except during famine. A decoction made from the boiled root has been regularly used to relieve pain following child birth. Legend has it that uses of the root can deter evil from entering a household. (1)
Despite a long history of humans consuming the plant, very little scientific research exists on it. If you search the PubMed database for Cucumis metuliferus, fewer than three dozen results come back. Most are related to things that are agricultural, not medicinal.
What follows are the health benefits of horned melon/kiwano fruit based on known nutrition facts, as well as the theoretical possibilities suggested by research.
1. Low calorie
According to the USDA National Nutrient Database, the average kiwano is just 92 calories. (2)
2. Low sugar
There’s about 16g of carbs in a horned cucumber and only a couple grams are in the form of sugar (fructose and sucrose).
3. High protein
Because it is rich in seeds, it is among the higher protein fruits. There’s an average of 3.72g of protein per fruit. That means 16% of the calories are coming from protein.
4. Moderate vitamin C
With 11 mg per fruit, each kiwano offers 18% of the adult daily value for vitamin C.
5. Some antioxidant activity
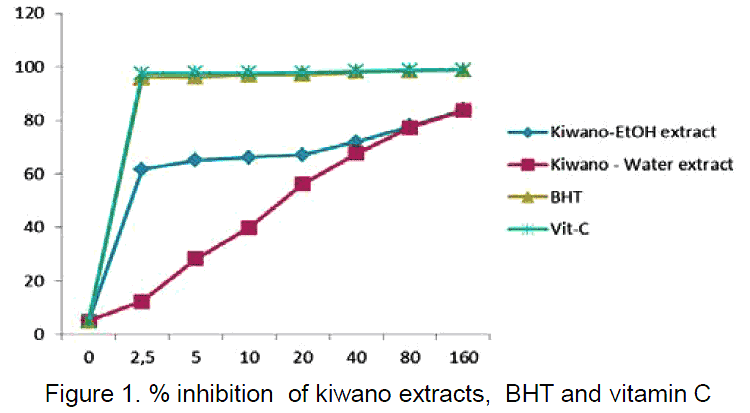
The horned melon is not a superfood for antioxidant content. When compared to other common fruits like apples, oranges, and grapes, it demonstrates less antioxidant activity according to DPPH radical scavenging capacity testing.
The above chart comes from a Turkish university, which measured the total phenolics and flavonoids, pitting their free radical scavenging ability against ascorbic acid (vitamin C) and butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT). The latter is widely used synthetic antioxidant. The performance of kiwano extract was minimal to moderate in comparison. (3)
While the vitamin C is responsible for most of the antioxidant activity, the yellowish-orange skin of kiwano fruits is a rich source of lutein, just like their relative the pumpkin. The other most prevalent antioxidant is called isovitexin 200-O-glucoside. (4) (5)
6. Rich in magnesium and iron
When it comes to essential minerals, the most noteworthy in kiwano are magnesium and iron, with 21% and 13% of the daily value, respectively. There are lower amounts of potassium, phosphorus, and zinc.
7. Hydrating
Approximately 89% of the kiwano is water, which ranks it among the fruits with the highest water content. They’re comparable to cantaloupe. They have slightly more than pineapple, raspberries, oranges, blueberries, and apples. Fruits and vegetables with higher water content include regular cucumbers, celery, lettuce, watermelon, and tomatoes.
8. May lower blood sugar
A Nigerian university published a study where they fed fruit pulp extract to regular rats and those with induced diabetes.
In the normal rats, there was no decrease in blood glucose levels. However in the diabetic rats, oral dosages of 1,000 and 1,500 mg/kg produced a significant decrease.
The mechanism wasn’t identified but the scientists suggested that the saponin glucosides might be responsible, since those have documented to have a blood sugar lowering effect in other research. (6)
9. Antibacterial activity
Lab research has reported the fruit to demonstrate inhibitory activity against Salmonella gallinarum bacteria. (7)
10. Antiviral activity
The non-bitter horned melon is eaten and the bitter version has been used in African traditional medicine practices for measles, chickenpox, herpes, HIV, and other viral diseases. There is no documented evidence or proof that those herbal remedies prevent, treat, or cure these diseases, or any other for that matter.
In theory, it is feasible that compounds in the plant might offer some medicinal potential, because tests using the isolated alkaloids were found to reduce the side effects of Newcastle disease, which is caused by a virus. However, it does appear to demonstrate high antiviral activity like some other plants do. (8)
Nutrition facts
| Horned Melon Nutrition Facts | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Serving Size: 1 fruit (209g) | |||
| Calories | 91 | ||
| % Daily Value* | % Daily Value | ||
| Total Fat 2.6g | 4% | Vitamin A | 6% |
| Sodium 0mg | 0% | Vitamin C | 18% |
| Potassium | 7% | Vitamin B6 | 5% |
| Total Carbohydrates 16g | 5% | Calcium | 2% |
| Protein 3.7g | Magnesium | 21% | |
| Iron | 13% | ||
| *Percent Daily Values (DV) are based on a 2,000 calorie diet | |||
How to pick
The best way how to tell if a kiwano is ripe is by the color of its skin. The melon ripens from green, to yellow, to yellowish-orange. Pick the latter. A ripe kiwano fruit will have a softer skin. An unripe yellow will be harder to the touch in comparison.
It’s best to store the uncut fruit at room temperature, not in the refrigerator. After cutting, you will need to refrigerate.
Ideally, you should consume within a few days of purchase. (9)
How to eat
Step 1: Rinse and dry
This is a niche fruit. You won’t find USDA certified organic kiwano for sale. All the more reason you should carefully rinse it in cold water. Even if you’re not eating the melon’s skin, the knife will pass through it and as you scoop out the pulp, the kiwano juice will carry off whatever is on the peel – whether for better or for worse!
The spikes can catch the fibers of paper towels. Using a regular towel to dry the fruit is preferable.
Step 2: Cut fruit in half lengthwise
With a cutting board and sharp knife, cut the kiwano lengthwise.
Or as they used to tell you in kindergarten… cut it the hot dog way, not the hamburger way!
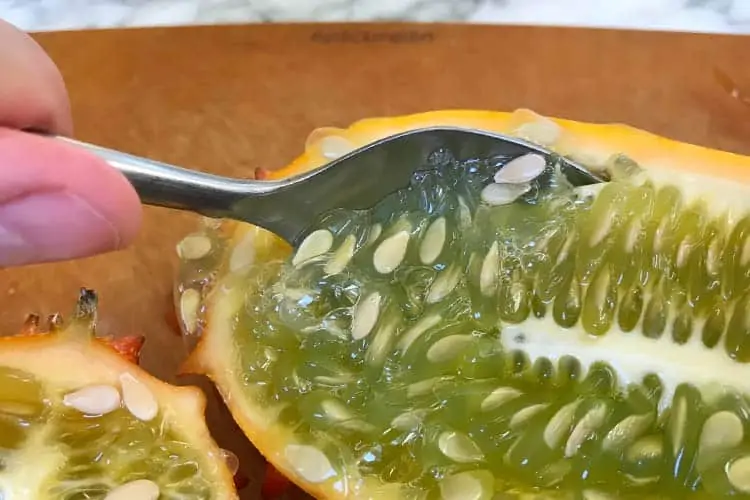
Step 3: Scoop out pulp with spoon
Using a tablespoon, dig into the green pulp where it meets the white skin.
You will be able to easily scoop out the pulp. Do this with one half at a time, while holding it above a bowl or other container to catch the prize.
Repeat process with the other half.
Step 4: Eat raw or in recipes
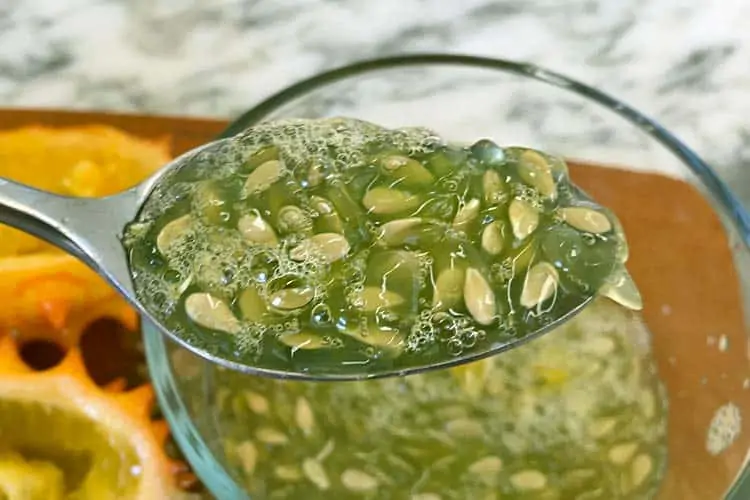
What you will be left with is a small dish of green pulp. Thicker than juice, but still liquid. Dispersed throughout will be hundreds of tiny seeds, just like those you find in a cucumber. You should eat the horned melon seeds because straining them out is quite a chore.
What is kiwano good for?
It doesn’t produce much edible pulp per fruit and at $5 apiece, it’s not an economical food.
The best use of kiwano horned melons are for presentation purposes; using the colorful and spiky skins to serve sorbets, gelatos, and fruit salads which include the pulp as a starring ingredient. Other good uses include the flavoring of cocktails, as the seeds are drinkable and offer a conversation starter. The pulp can be used for flavoring smoothies, sauces, and dressings. Make use of it in recipes for gazpacho and salsa. You can eat a kiwano raw or cooked.
Where to buy
What country does kiwano come from? Primarily Nigeria, Senegal, Namibia, Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe, South Africa, and Swaziland. In those countries, you can find the African horned melon for sale at fruit markets.
We never came across them while traveling in Botswana, Zambia, and South Africa during their summer (February). Even though it was in-season, it’s not considered to be a highly desirable fruit relative to others. It’s sold cheap.
In contrast, it’s one of the most expensive fruits when you find it for sale in America, Canada, and the United Kingdom. While they may not stock it regularly, even the common grocers carry kiwano fruit on occasion.
At a Ralph’s (Kroger) in Southern California, we spotted them for sale at $5 apiece. The Vons in La Jolla, CA also sell them. It’s been seen at Sprout’s in Bethany, OK and Whole Foods in Centerville, OH. Those sold in the US primarily come from New Zealand.
Assuming management is accommodating, the horned melon can be special ordered through any grocery store which carries Frieda’s and Melissa’s. Those produce brands are distributed nationwide at many supermarket chains.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.